Figure 6.
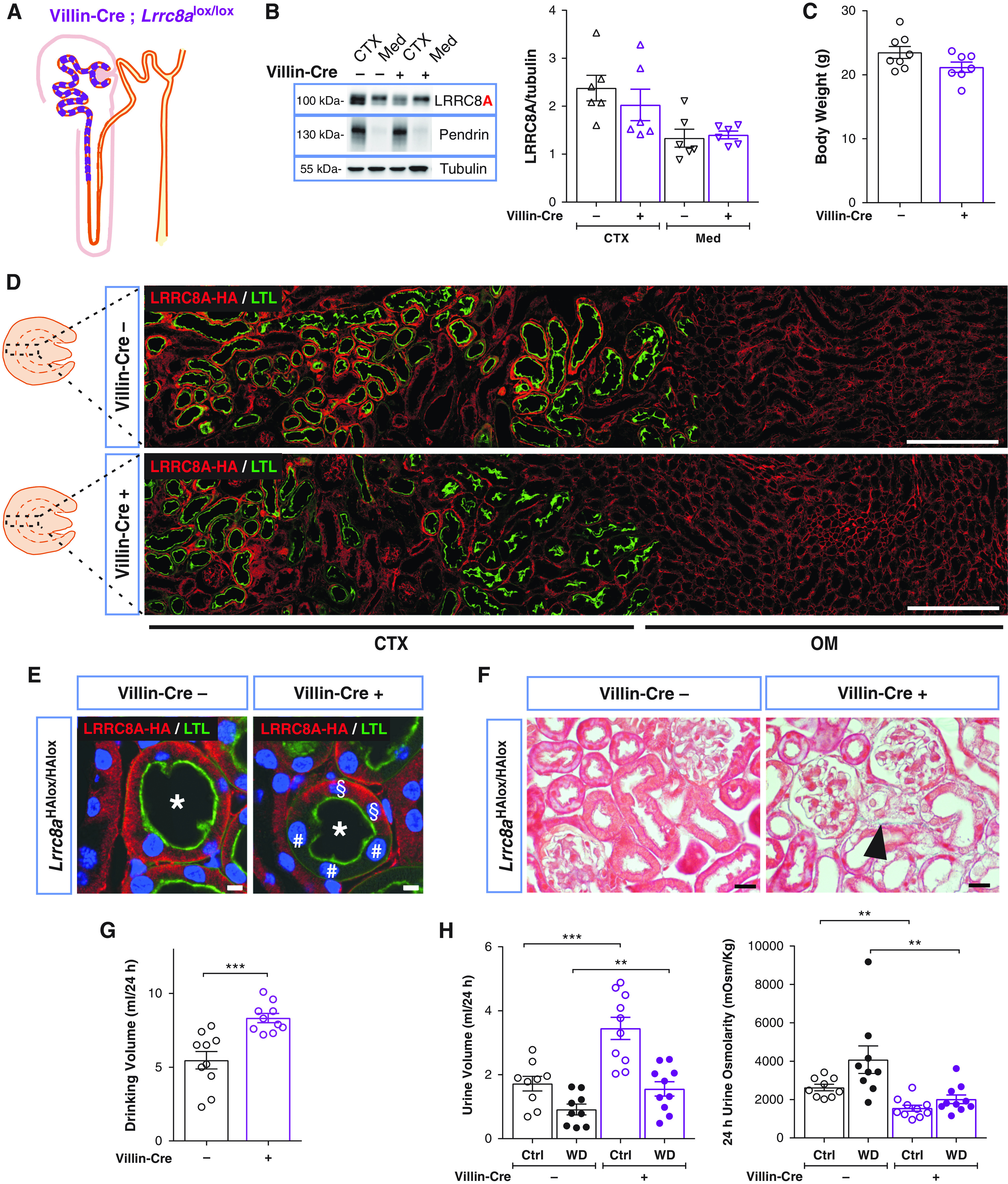
Proximal tubular–restricted disruption of LRRC8A in Villin-Cre;Lrrc8aHAlox/HAlox mice results in polyuria and polydipsia. (A) Sketch of chimeric deletion by Villin-Cre in the proximal nephron. (B) Left, Western blot analysis of LRRC8A expression in cortex (CTX) and medulla (Med) in Villin-Cre;Lrrc8aHAlox/HAlox and control (Lrrc8aHAlox/HAlox) mice. Pendrin, CTX marker; Tubulin, loading control. Right, Western blot quantification. (C) Body weight of control and Villin-Cre;Lrrc8aHAlox/HAlox 11- to 12-week-old siblings. (D) Assessment of Villin-Cre-driven LRRC8A deletion by HA labeling (red) of kidney sections from Villin-Cre;Lrrc8aHAlox/HAlox and control mice. PTs identified by Lotus tetragonolobus Lectin (LTL) (green). Quantification of deletion efficiency by cell counting yielded 48.7±2.6% in Villin-Cre;Lrrc8aHAlox/HAlox PT cells (using three images from two different mice). Cortex (CTX) and outer medulla (OM) indicated below. Scale bar, 200 μm. (E) Chimeric deletion (#) of basolateral HA-tagged LRRC8A (red) in Villin-Cre;Lrrc8aHAlox/HAlox mice. Cells expressing LRRC8A-HA indicated with §, nuclei stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 5 μm. (F) Masson’s trichrome staining of kidney cortex from control and Villin-Cre mice. Tubular injury in Villin-Cre mice with very mild fibrosis (blue), and few swollen cells (black arrowhead). Scale bar, 20 µm. (G) Daily water intake in Villin-Cre;Lrrc8alox/lox and control mice. (H) Volume and osmolarity of 24-hour urine of Villin-Cre and control mice with water ad libitum (Ctrl) or under 24-hour water restriction (WD). Bars, mean±SEM, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (Mann–Whitney U test). Pictures are representative of more than three mice per group.
