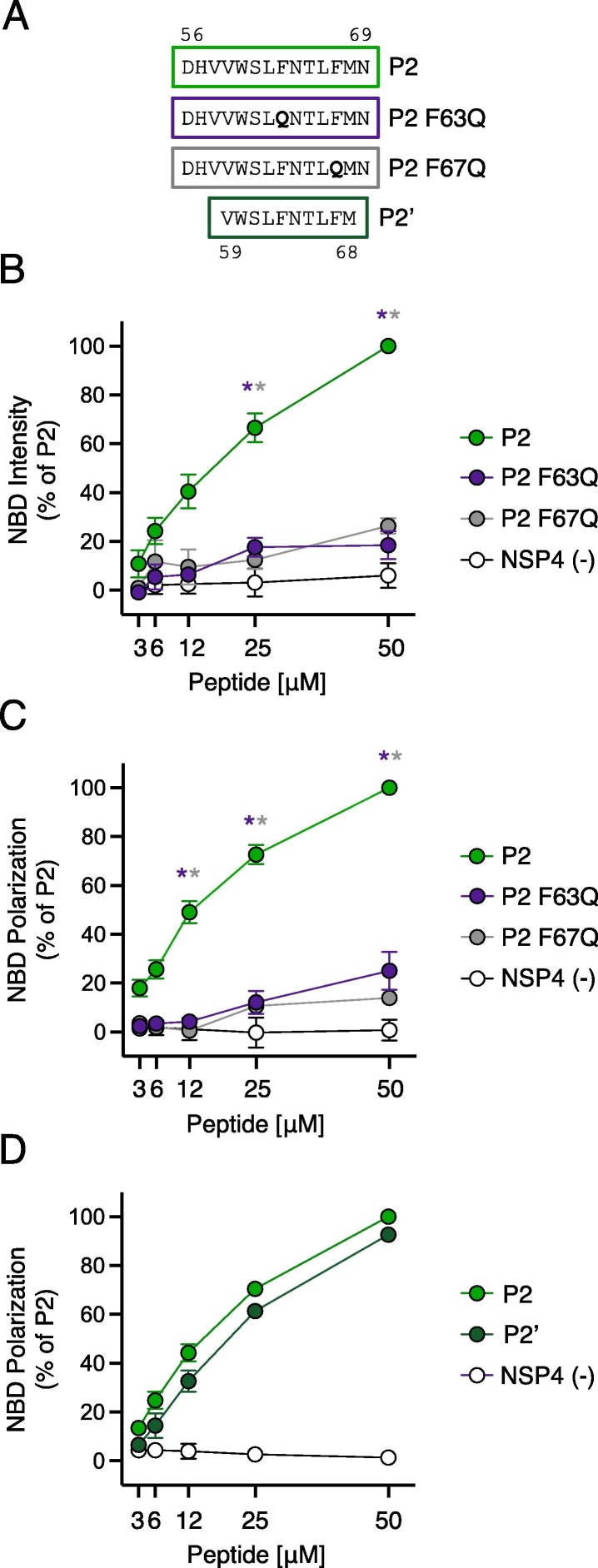
Figure 4.
Loss-of-function mutations in IFITM3 disrupt cholesterol binding. (A) Detailed view of peptide sequences. Numbers correspond to amino acid residues in the context of full-length IFITM3. (B) NBD-cholesterol (500 nM) fluorescence intensities measured by spectroscopy (excitation. 470 nm; emission. 540 nm) following incubation with increasing concentrations (3.125–50 μM) of indicated peptides. Results represent the mean of three independent experiments and are normalized to 50 μM P2 peptide + NBD-cholesterol (set to 100%). (C) Fluorescence polarization of NBD-cholesterol (500 nM) measured by spectroscopy (excitation with plane-polarized light. 470 nm; emission. 540 nm) following incubation with increasing concentrations (3.125–50 μM) of indicated peptides. Results represent the mean of three independent experiments and are normalized to 50 μM P2 peptide + NBD-cholesterol (set to 100%). (D) Fluorescence polarization of NBD-cholesterol (500 nM) following incubation with increasing concentrations (3.125–50 μM) of P2, P2′, or control peptide. Results represent the mean of three independent experiments and are normalized to 50 μM P2 peptide + NBD-cholesterol (set to 100%). Error bars indicate standard error. Asterisks indicate statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) between P2 and another peptide (condition indicated by asterisk color), as determined by one-way ANOVA.