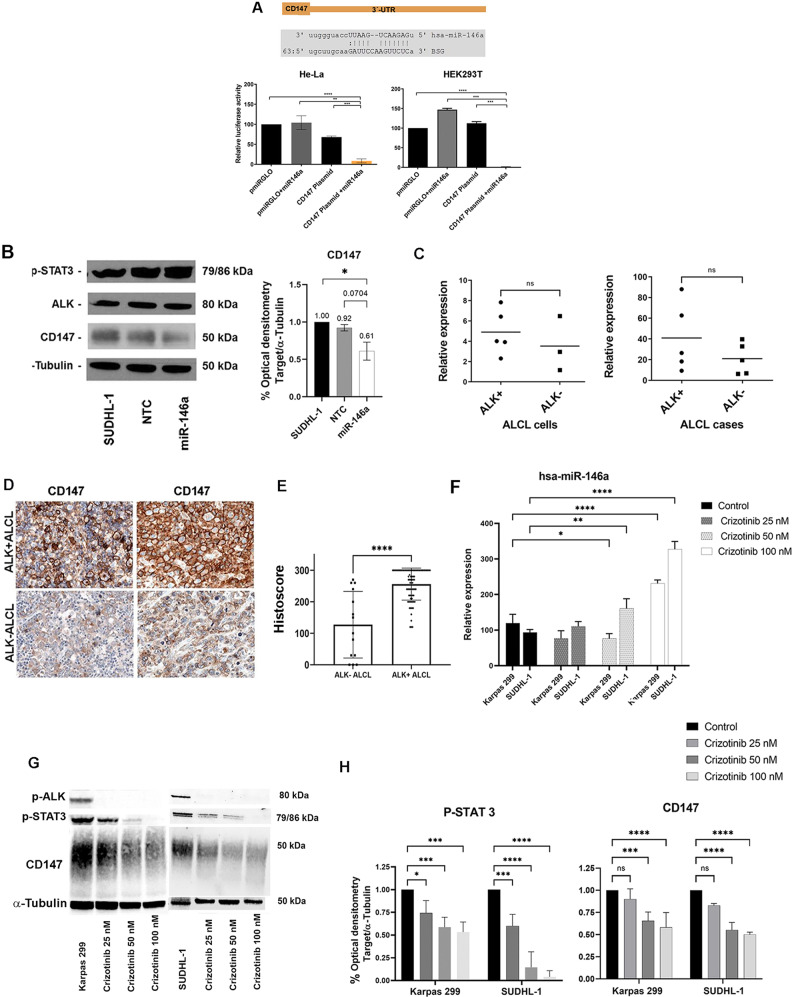
Fig. 2. CD147 is a target gene of mi-146a and is differentially expressed in ALK+ and ALK− ALCL.
A Luciferase activity using the pmirGLO Vector containing CD147 region targeted by miR-146a. Upper panel illustrates miR-146a binding site within the 3´-UTR of CD147 according to miRanda prediction tool (www.microrna.org/). Lower panel displays the dual luciferase reporter assay performed in HeLa and HEK293-T cells co-transfected using the pmiRGLO vector with and without CD147-3´-UTR construct. Relative luciferase activity was measured in triplicates (firefly LUC / renilla LUC) after 40 h of transfection. Columns represent mean luciferase activity in HEK293-T and HeLa cells transfected. For statistical Unpaired t-test was used, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. B Western blot analysis of ALK, p-STAT-3 and the miR-146a target protein CD147 in ALK+ ALCL SUDHL-1 cells with miR-146a transfection in comparison to controls (SUDHL-1 untransfected and transfected with non-targeted mi-RNA). Western blot analysis demonstrates reduced CD147 protein and unaffected expression of ALK and p-STAT3 after miR-146a overexpression. Each lane contained 15 µg protein extract. α-Tubulin was used as loading control. CD147 quantification was obtained from independent biological triplicate samples and measured by optical densitometry. Values were normalized to α-tubulin and represented in the bar graph. For statistical analysis unpaired t-test was used, *p < 0.05. C mRNA levels of CD147 were investigated in five ALK+ (SUDHL-1, KiJK, Karpas 299, SUP-M2 and SR-786) and three ALK− (Mac-1, Mac2a and FE-PD) ALCL cell lines and in five primary ALK+ and ALK− ALCL cases using RT-qPCR. RT-qPCR quantification values were normalized to ACTB. Results are depicted as plots representing the ratio of ACTB/ target gene Cp-values, each point represents the average of three independent measurements. For statistical analysis a Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used (p = 0.28 and p = 0.21, respectively). D. ALK+ ALCL cases display strong and homogenous membranous CD147 expression. In contrast, ALK− ALCL cases reveal a weaker expression of CD147 (Immunohistochemistry; original magnification 400×). E Immunohistochemistry quantification of CD147 staining in primary cases: 81 cases ALK+ ALCL and 14 ALK− ALCL cases. Every point represents a case. For statistical analysis a Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used, ****p < 0.0001. F RT-qPCR analysis of relative miR-146a expression levels in corresponding ALCL cells with increasing doses of NPM-ALK inactivation. Each bar represents the average of biological triplicates. For statistical analysis unpaired t-test was used, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. G Western blot analysis of p-ALK, p-STAT-3 and CD147 in ALK+ ALCL cell lines (SUDHL-1 and Karpas 299) after 48 h treatment with different doses of Crizotinib, as indicated. Untreated cells were loaded as control. Western blot analysis demonstrates a complete absence of ALK activity after Crizotinib treatment and a reduction of CD147 and p-STAT3 protein expression. Each lane contained 25 µg protein extract. α-Tubulin was used as loading control. H Quantification of p-STAT3 or CD147 obtained from independent biological triplicate samples, normalized to α-Tubulin and represented in the bar graph. For statistical analysis unpaired t-test was used, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.