FIG. 1.
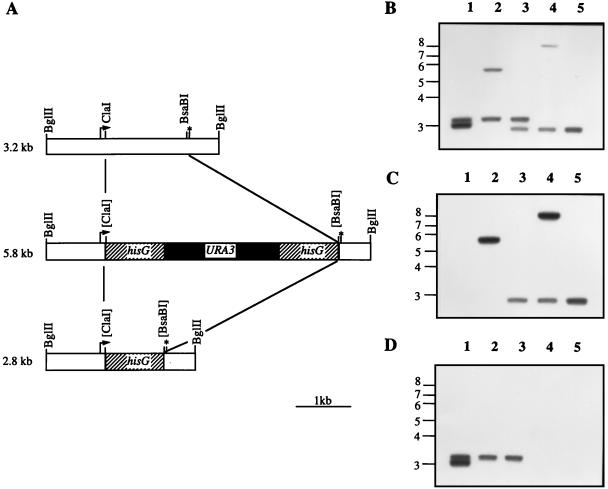
Chromosomal deletion of CAP1 in CAI4. (A) Schematic representation of the disruption strategy. The CAP1 locus is contained within a 3.2-kb BglII fragment (top). The start (arrow) and stop (asterisk) codons of the CAP1 ORF are indicated. The disruption cassette (middle) was generated by replacing a 1.35-kb ClaI-BsaBI CAP1 fragment by the 4-kb hisG-URA3-hisG cassette. After counterselection on 5-FOA, recombination between the two hisG direct repeats should generate a 2.8-kb BglII fragment (bottom). Southern blot analysis was used to characterize the different steps of the disruption (B to D). Genomic DNA was extracted from strains CAI4 CAP1/CAP1 (lanes 1), CJD10 CAP1/cap1Δ::hisG-URA3-hisG (lanes 2), CJD11 CAP1/cap1Δ::hisG (lanes 3), CJD20 cap1Δ::hisG-URA3-hisG/cap1Δ::hisG (lanes 4), and CJD21 cap1Δ::hisG/cap1Δ::hisG (lanes 5). DNA samples (2 μg) were digested in triplicate with BglII, separated by electrophoresis on agarose gels, and transferred to nylon membranes. The blots were then probed with either the 3.2-kb BglII fragment comprising the entire wild-type CAP1 gene (B), a 0.9-kb BamHI-BglII hisG fragment (C), or a 0.6-kb XbaI-HincII CAP1 internal fragment deleted in the cap1Δ::hisG-URA3-hisG allele (D). Positions of molecular size markers (in kilobases) are indicated on the left. Membranes were exposed for 6 h at −80°C with two intensifying screens.