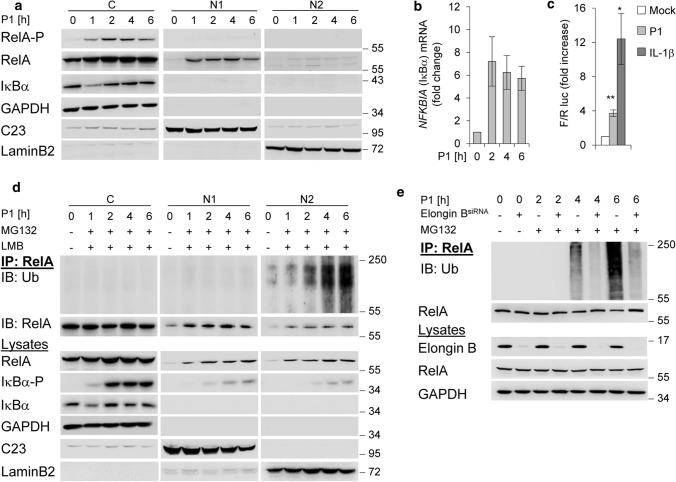
Fig. 1.
NF-κB/RelA turnover in H. pylori infection. a AGS cells were infected with H. pylori for the indicated times. Subcellular fractions were subjected to IB for analysis of the indicated proteins. b Total RNA was isolated from H. pylori-infected AGS cells and analysed using quantitative RT-PCR for the NFKBIA (the gene of IκBα) transcript. Data shown depict the average of triplicate determinations normalized to GAPDH housekeeping gene. Error bars denote mean ± SD. c AGS cells were transfected with luciferase reporters, treated with H. pylori or IL-1β (10 ng/ml) and fold increase of NF-κB transactivation activity (Firefly/Renilla luc) analysed after 3.5 h in a transactivation assay. d RelA-IP from subcellular fractions of H. pylori-infected AGS cells treated with MG132 and LMB 30 min after infection. The RelA-IP was performed at the indicated times in the presence of NEM and OPT, followed by IB analysis of the indicated proteins. e AGS cells were transfected with siRNA against Elongin B and infected with H. pylori for the indicated times (MG132 was added 30 min after infection). IP with an anti-RelA or isotype-matched antibody (IgG) was performed at the indicated times in the presence of NEM and OPT, followed by IB analysis of the indicated proteins. Data information: Data shown in (a, d, e) are representative for at least two independent experiments. Data shown in (b, c) are from one experiment with three technical replicates. GAPDH, C23 and LaminB2 served as load controls and indicate the purity of the subcellular fractions