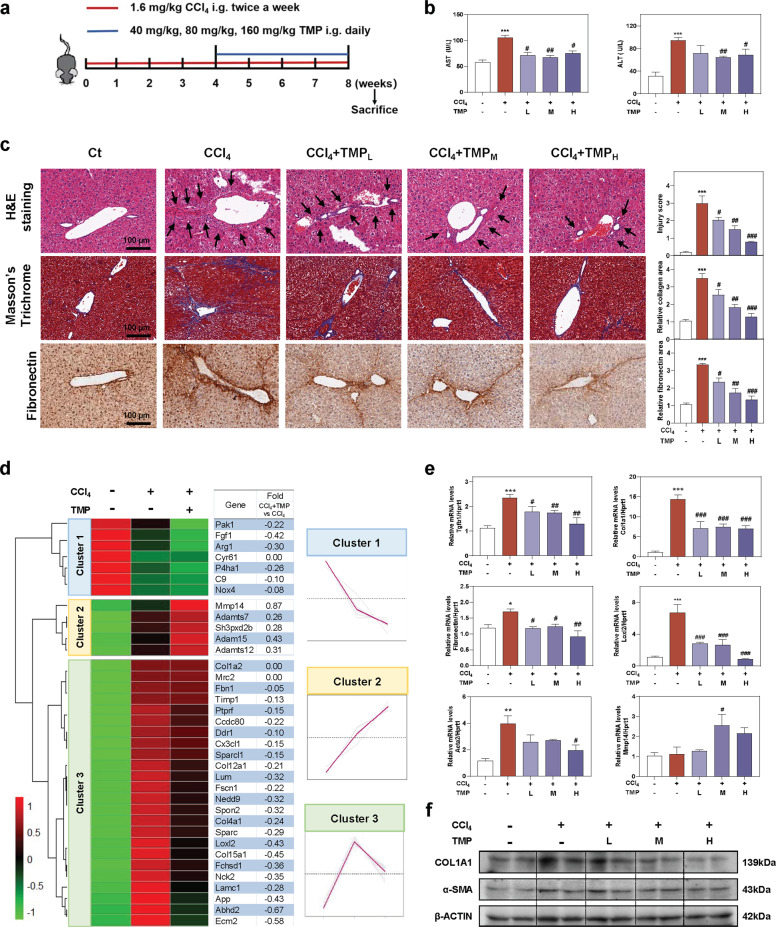
Fig. 1. TMP ameliorates CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis and liver injury.
Mice were administered CCl4 (1.6 mg/kg) and different dosages (40, 80, and 160 mg/kg) of TMP by gavage. a Experimental protocol. b AST and ALT levels in serum. c Representative images of H&E, Masson’s Trichrome, and fibronectin staining. The immunostaining was quantified by Image J software. Scale bar = 100 µm. d The relative expression levels of DEGs enriched in ECM synthesis and degradation pathways were shown as a heatmap. Average log2 fold changes of CCl4 + TMP vs CCl4 groups were presented in the right panel. The expression of DEGs was classified into three clusters and the trend lines presenting the hepatic changes of these DEGs were shown. e Relative mRNA levels of Tgfb1, Col1a1, Fibronectin, Loxl2, Acta2, and Mmp14 were determined by qPCR and normalized using Hprt1 as an internal control. f Representative immunoblots against COL1A1, α-SMA, and β-ACTIN were shown. Statistical significance: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, compared with control group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, compared with CCl4 group (n = 6).