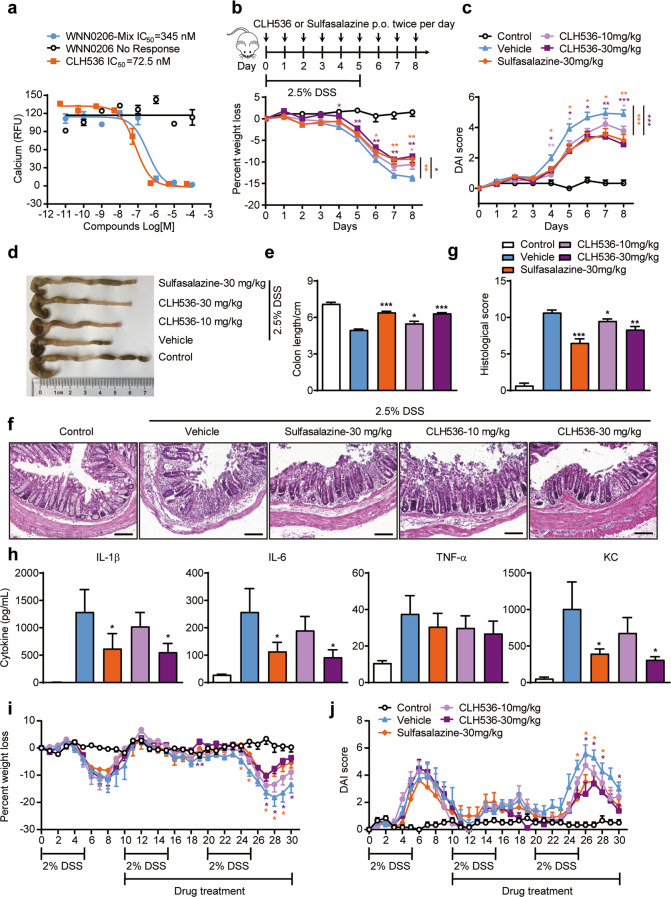
Fig. 2. GPR84 receptor antagonist alleviates pathogenesis of DSS-induced colitis in mice.
a Dose–response of CLH536, WNN0206-Mix, and WNN0206 in inhibiting 6-OAU-induced calcium responses in HEK293/Gα16/GPR84 cells. b, c Change in the body weight (b) and DAI score (c) of DSS-treated mice receiving vehicle, sulfasalazine (30 mg/kg) and CLH536 (10 or 30 mg/kg) by oral administration (n = 18), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (two-way ANOVA with Mann–Whitney U-test) vs. DSS-induced mice receiving vehicle. d, e Representative photographs (d) and statistical analysis of the length (e) of colons at day 7 after treatment. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 vs. DSS-induced mice receiving vehicle. f, g Representative images of H&E-stained colon sections (f) and statistical analysis of histological scores (g) at day 7 after various treatments (n = 12). Scale bars = 50 μm, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. DSS-induced mice receiving vehicle. h Cytokine production in the colon at day 7 after various treatments (n = 12), *P < 0.05 vs. DSS-induced mice receiving vehicle. i, j Change in the body weight (i) and DAI score (j) in mice with DSS-induced chronic colitis receiving vehicle, sulfasalazine (30 mg/kg) and CLH536 (10 or 30 mg/kg) by oral administration started on Day 10 (n = 8), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (two-way ANOVA with Mann–Whitney U-test) vs. DSS-induced mice receiving vehicle. All data are expressed as means ± SEM.