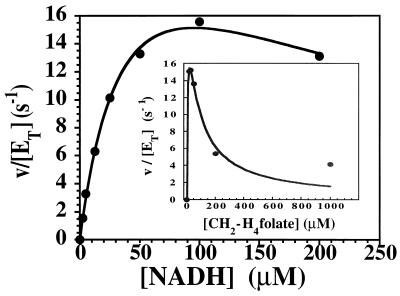
FIG. 4.
Measurement of turnover in the NADH-CH2-H4folate oxidoreductase reaction at 15°C. Under anaerobic conditions in a stopped-flow spectrophotometer, enzyme, 20 μM in 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) containing 10% glycerol and 0.3 mM EDTA, was mixed with an equal volume of the same buffer containing 30 μM (6R)CH2-H4folate and various concentrations of NADH. The initial velocity, measured as the rate of reduction of the enzyme at 447 nm, is plotted against the NADH concentration after mixing. The inset shows a plot of the initial velocity, measured as the rate of formation of NADH at 340 nm, determined when 20 μM enzyme was mixed with an equal volume of buffer containing 200 μM NADH and various concentrations of CH2-H4folate [added as a (6R,S)CH2-H4folate mixture]. Marked excess substrate inhibition is evident. Using equation 2, the solid-line fits to the data were determined, yielding the following values for kinetic parameters: KmA (NADH), 13 ± 2 μM; KiA, 9 ± 2 μM; KmB [(6R)CH2-H4folate], 0.8 ± 0.2 μM; KiB, 7.1 ± 1.4 μM; and Vmax/ET, 30 ± 3 s−1.