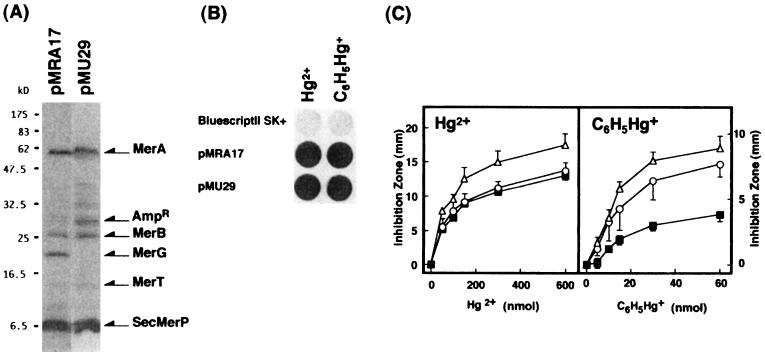
FIG. 2.
mer polypeptides (A), mercury volatilization (B), and mercury resistance encoded by deletion plasmid pMU29. (A) E. coli CSR603 harboring pMRA17 or pMU29 was cultured, induced with 1 μM Hg2+, UV irradiated, and labeled with [35S]methionine. Labeled cells were collected and lysed, and proteins were analyzed on SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Molecular mass markers are indicated to the left. The arrows marked MerA, MerB, MerG, MerT, and SecMerP indicate the polypeptides of the respective genes. (B) Cells were grown, induced with 1 μM Hg2+, and harvested. Volatilization of mercury from mercurials was detected by the X-ray film method as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Resistance of E. coli XL1-Blue with pMRA17 (■), pMU29 (○), and pBluescriptII SK+ (▵) to mercuric chloride and phenylmercuric acetate was determined by measuring the diameter of the inhibition zone (minus the 6.5-mm disk diameter) on petri dishes after overnight growth at 37°C. All values are the means of triplicate experiments.