Fig. 5. Urgent and non-urgent color-discrimination tasks.
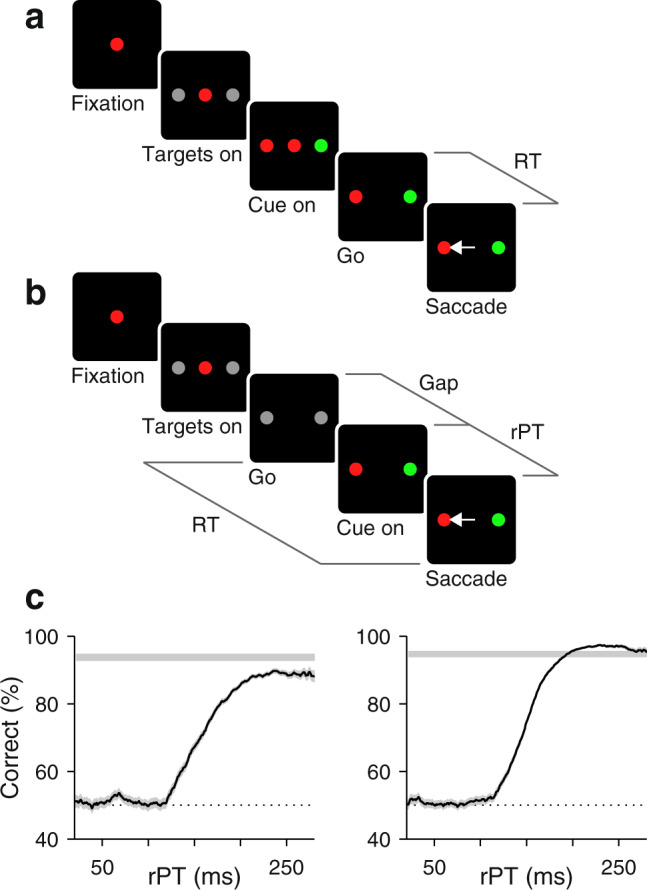
Subjects had to look to the peripheral target that matched the color of the fixation point. a Easy, non-urgent task. The color stimuli are presented first (Cue on), and after 500–1000 ms, the go signal (fixation point offset; Go) is given. b Urgent task. The go signal is given first, before the cue is revealed. All time parameters and intervals are as in the CRDM task (Fig. 1c). c Tachometric curves based on all the recording sessions during which the urgent color-discrimination task was performed by monkeys C (left, 7330 trials) and T (right, 10,745 trials). Each point includes trials within a 51 ms rPT bin. Traces show percentage of correct choices across trials in each bin, and shaded error bands indicate ±1 SE. Gray horizontal strips indicate performance in the non-urgent task (95% confidence interval). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
