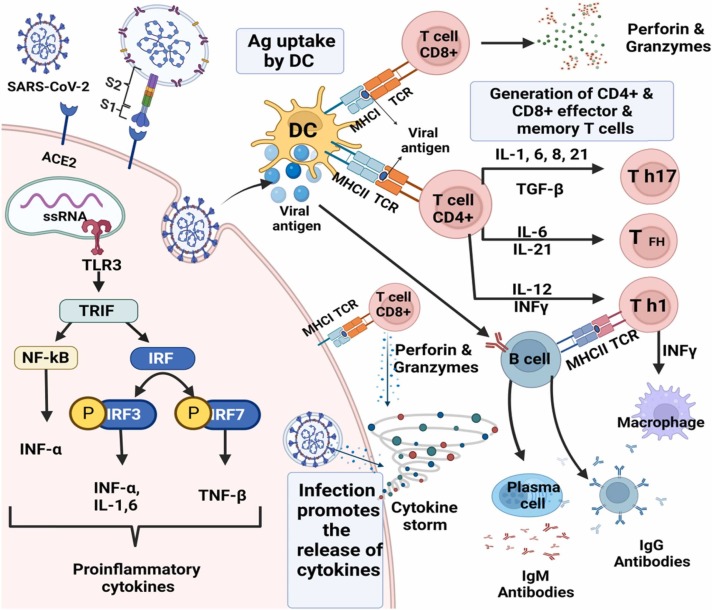
Fig. 2.
Immune response during COVID-19 disease. SARS-CoV-2 leads to infection of ACE2 expressing target cells such as alveolar type 2 cells or other unknown target cells. the virus may inhibit anti-viral IFN responses resulting in uncontrolled viral replication. The flow of neutrophils and monocytes/macrophages results in the hyper-production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The immunopathology of the lung may be the result of the “cytokine storms”. Specific Th1/Th17 may be activated and contributes to exacerbating inflammatory responses. B cells/plasma cells produce SARS-CoV-2 specific antibodies that may help neutralize viruses.