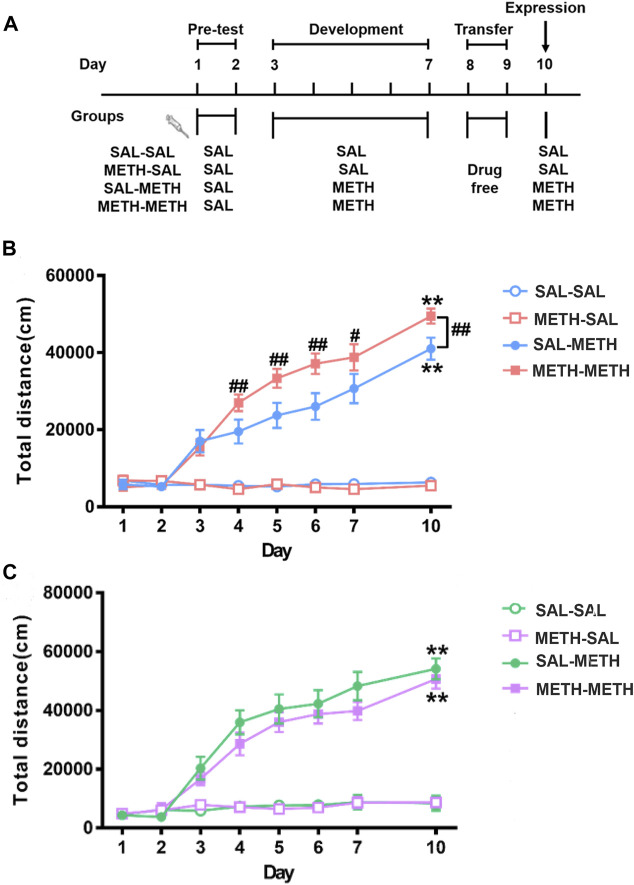
FIGURE 2.
Maternal METH exposure enhanced METH-induced behavioral sensitization in F1 adult male progeny. (A) Schematics of METH-induced locomotor sensitization. (B) METH- METH male mice developed an earlier locomotor sensitization and exhibited hyper-locomotor activity compared with SAL-METH males. (C) METH-METH female mice developed a trend of reduced behavioral sensitization compared with SAL-METH females. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA with a post hoc multiple comparisons was used. **p < 0.01 compared with day 3; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 compared with SAL-METH group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (each group n = 8). Abbreviations: SAL-SAL, prenatal and postnatal saline exposure; METH-SAL, prenatal METH and postnatal saline exposure; SAL-METH, prenatal saline and postnatal METH exposure; METH-METH, prenatal and postnatal METH exposure.