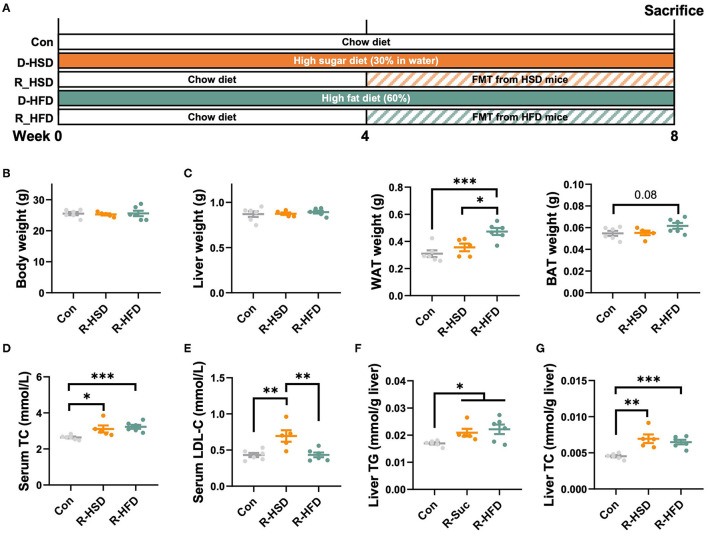
Figure 6.
High-fat and high-sucrose diet-induced lipid metabolic dysregulation is gut microbiota-dependent. (A) Male C57BL/6J mice (4 weeks old) were, respectively, treated with chow diet (Con), high-sucrose-diet (D-HSD), or high-fat diet (D-HFD) for 4 weeks, and then, fecal bacteria collected from donor mice in each group were pooled and an equal volume was orally transplanted to recipient mice (R-HSD, R-HFD), respectively, at following 4 weeks. Recipient mice were fed with chow diet throughout the experiment. (B) Body weight (g). (C) Tissue weight, including liver, WAT, and BAT (g). (D) Serum TC level (mmol/L). (E) Serum LDL-C level (mmol/L). (F) Hepatic TG level (mmol/g liver). (G) Hepatic TC level (mmol/ g liver). Data are represented as the mean ± SEM. n = 5-6; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.