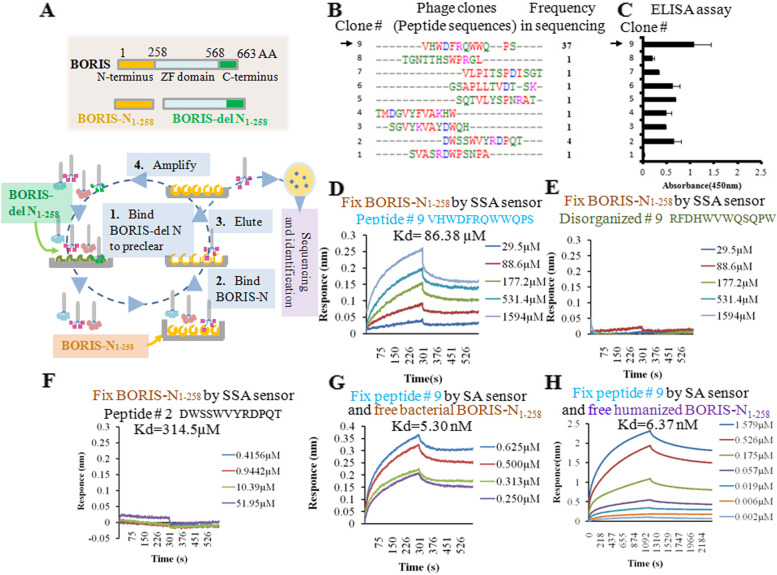
Fig. 1.
Selection and characterization of the BORIS-binding peptide. (A) Procedure for the selection of BORIS-binding peptides. (B) The sequences and frequencies of the peptides enriched after elution. (C) ELISA testing the affinity of phages for the BORIS-N1-258 protein. (D) The peptide from phage clone 9 was used to determine the affinity of the interaction with BORIS-N1-258 protein by BLI. The panel shows the test of the BORIS-N1-258 protein immobilized on an SSA sensor and free peptide in solution. (E) Scrambled peptide 9 showing no affinity to BORIS-N1-258 in the BLI assay. (F) Peptide 2 showed a weak binding affinity (Kd) of 314.5 µM to BORIS-N1-258 in the BLI assay. (G) Peptide 9 immobilized on an SA sensor and free BORIS-N1-258 protein in solution. (H) The BORIS-N1-258 protein purified from HEK293 cells was used to examine the interaction with synthesized peptide 9. The test was performed by fixing peptide 9 on an SA sensor and releasing the humanized BORIS-N1-258 protein to solution in a BLI assay