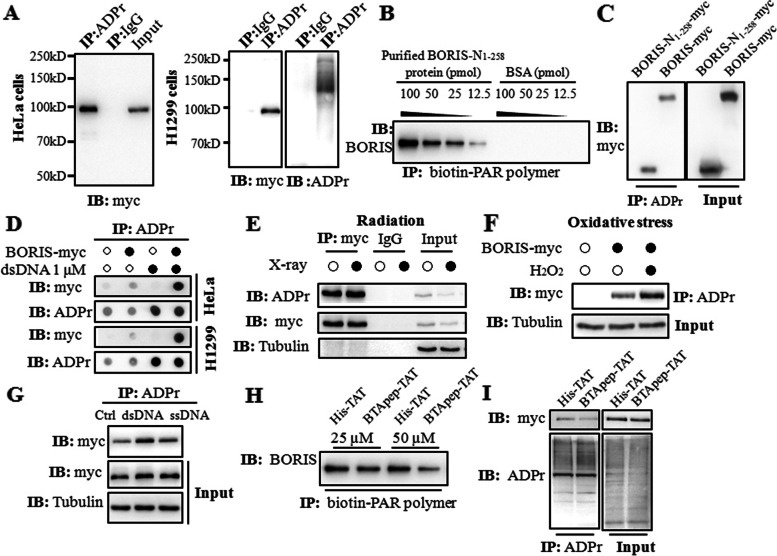
Fig. 4.
BTApep-TAT inhibited the ADP ribosylation of BORIS in response to DNA damage. (A) ADP-ribosylation of BORIS was determined in BORIS-myc-transfected HeLa and H1299 cells using the ADPr antibody, which detected both poly-ADPr and mono-ADP-ribosylation. (B) The purified BORIS-N1-258 protein or BSA was diluted and incubated with 5 pmol of biotin-PAR polymers immobilized on streptavidin beads. Specific interaction was observed with the BORIS-N1-258 protein, but not with BSA. (C) ADP-ribosylation of BORIS-N1-258-myc was determined in transfected H1299 cells. The levels of ADP ribosylation were nearly identical for BORIS-N1-258 and full-length BORIS. (D) The plasmids of BORIS-myc or empty vector were transfected into H1299 and HeLa cells. The crude nuclear extracts were supplemented with 1 μM dsDNA. BORIS was ADP-ribosylated in both H1299 and HeLa cells, and ADP-ribosylation was enhanced upon dsDNA induction. (E) DNA damage was induced in H1299 cells by 30 Gy X-ray irradiation. (F) DNA damage was induced in H1299 cells by treatment with H2O2 at a concentration of 500 µM for 10 min. (G) The levels of ADP ribosylation of BORIS-myc in H1299 cells were compared between dsDNA and ssDNA treatments. (H) ADP ribosylation of BORIS-N1-258 was examined by an in vitro ADP-ribosylation assay. BTApep-TAT treatment significantly suppressed ADP ribosylation of BORIS-N1-258. (I) ADP ribosylation of BORIS-myc in H1299 cells after treatment with 25 µM BTApep-TAT or His-TAT was examined by immunoprecipitation of ADP-ribosylated protein and immunoblotting against the myc tag