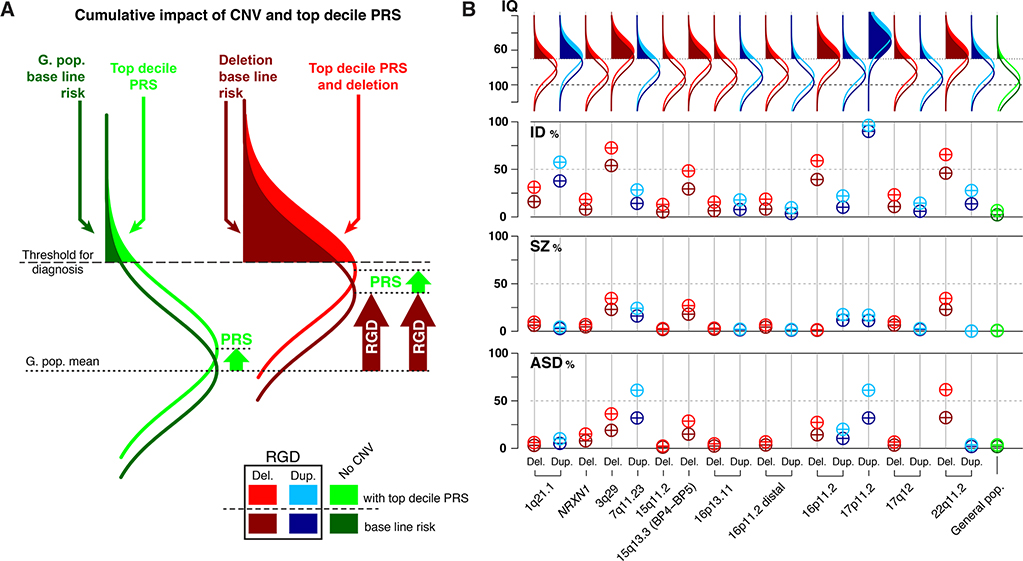
Figure 2.
Risk prediction in rare CNV carriers with and without polygenic risk (PRS) information.
(A) Schematic showing baseline risk for the general population (dark green) and a large effect size RGD (dark red). Risk for individuals of both groups with a top decile PRS score (light green and light red). Although the PRS has the same small effect size in both groups, it results in a larger increase in the penetrance of a diagnosis in the RGD group. (B) Comparing risk conferred by CNVs for carriers without PRS information (baseline risk, table 1) to those with top decile PRS values. For schizophrenia PRS, OR= 1.5 (23, 59). For Autism spectrum disorder PRS, OR = 1.91 (96). Effect size of top decile PRS cognitive ability compared to 50th percentile = 0.45 z-score (23, 97). Risk in RGD carriers with top decile PRS values is computed based on an additive model. Y-axis for IQ: IQ values. Y-axis for ID, SZ, and ASD: penetrance (from 0 to 100%) of a diagnosis in CNV carriers.