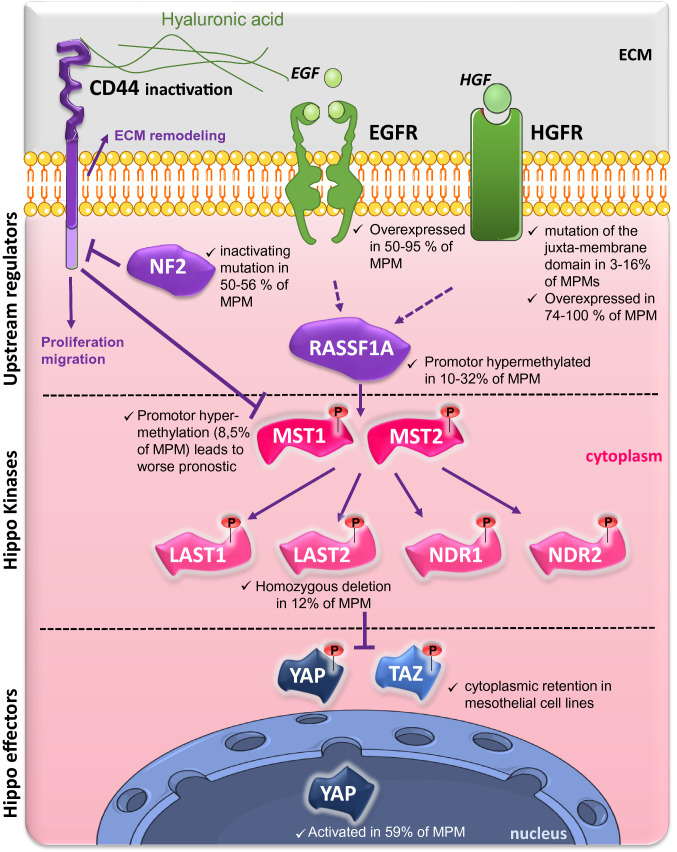
Fig. 2.
Indexed alterations of the expression of members of the RASSF1A/Hippo pathway in malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) at a glance. In mammals, the Hippo pathway is subdivided into three groups of proteins: upstream regulators (CD44, NF2, RASSF1A), the core kinases (MST and NDR [nuclear Dbf2-related kinase]) and their respective adapters (not shown) and the end effectors, namely YAP (Yes-associated protein) and its paralogous TAZ (transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif). CD44, linked to hyaluronic acid (HA), a glycosaminoglycan found abundantly in the pleural cavity leads to cell proliferation/invasion. In healthy mesothelial cells, NF2 negatively regulates the CD44-HA (HA) interaction and thus the pro-tumorigenic activity of CD44 [171], but in MPM, NF2 is inactive in near 50% of MPM [59, 71, 92]. The intracellular segment of CD44 also fixes MST and prevents its action, thus, YAP/TAZ activity cannot be inhibited by their phosphorylation by LATS kinases [172]. Next to this direct inhibition of the activity of Hippo kinases, there are losses of expression of MST1 (MST1 promoter is methylated in 8.5% of MPM cases and leads to worse prognostic of patient [252]) and LATS2 (homozygous deletion mutations are found in 12% of the MPM [250]). Each of these anomalies results in an aberrant activation of YAP, that why, YAP has been shown to be constitutively activated in 59% of patients with MPM [254] while TAZ is reported to be sequestered in cytoplasm from MPM cell lines [252]. CD cluster of differentiation, ECM extracellular cell matrix, EGF epidermal growth factor, EGFR EGF receptor, HGFR hepatocyte growth factor receptor, LATS large tumor suppressor kinase, MST mammalian Ste20-like serine/threonine kinase, NDR nuclear Dbf2-related kinase, TAZ transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif, YAP Yes-associated protein