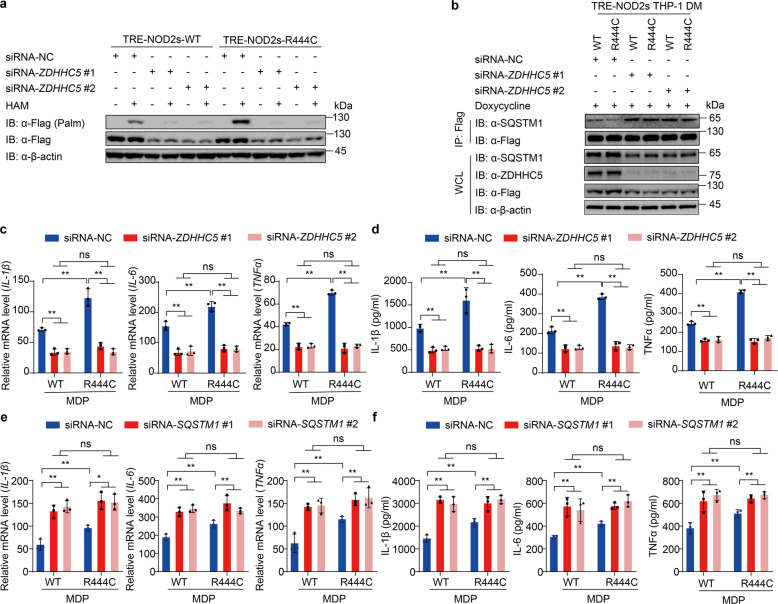
Fig. 6. Inhibition of NOD2s-R444C S-palmitoylation reverses NOD2s-induced excessive inflammatory responses.
a NOD2s-WT/R444C THP-1 cells were differentiated with PMA (100 ng/ml) overnight. After replacement of fresh medium supplemented with Dox (NOD2s-WT, 140 ng/ml; NOD2s- R444C, 100 ng/ml) for 12 h, cells were transfected with siRNA-NC or ZDHHC5 siRNAs for 36 h. Streptavidin blot detection of palmitoylated NOD2s-WT/R444C by ABE assay with or without HAM (1 M). b Immunoblot analysis showing the interaction of SQSTM1 and NOD2-WT/R444C in THP-1-DM cells supplemented with Dox (100 ng/ml) for 12 h. c, d Real-time PCR for IL-1β, IL-6 and TNFα transcription (c) and ELISA for IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα secretion (d) in MDP (10 μg/ml)-induced NOD2s-WT/R444C THP-1-DM cells with knockdown of ZDHHC5. e, f Real-time PCR for IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα transcription (e) and ELISA for IL-1β, IL-6 and TNFα secretion (f) in MDP (10 μg/ml)-induced NOD2s-WT/R444C THP-1-DM cells with knockdown of SQSTM1. In b–f, Dox was used at 100 ng/ml for both NOD2s-WT and NOD2s-R444C THP-1-derived macrophages. In c–f, all error bars, mean values ± SEM, P values were determined by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test of n = 3 independent biological experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns not significant. For a, b, similar results are obtained from three independent biological experiments.