Figure 1. Beclin1 enhances RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation.
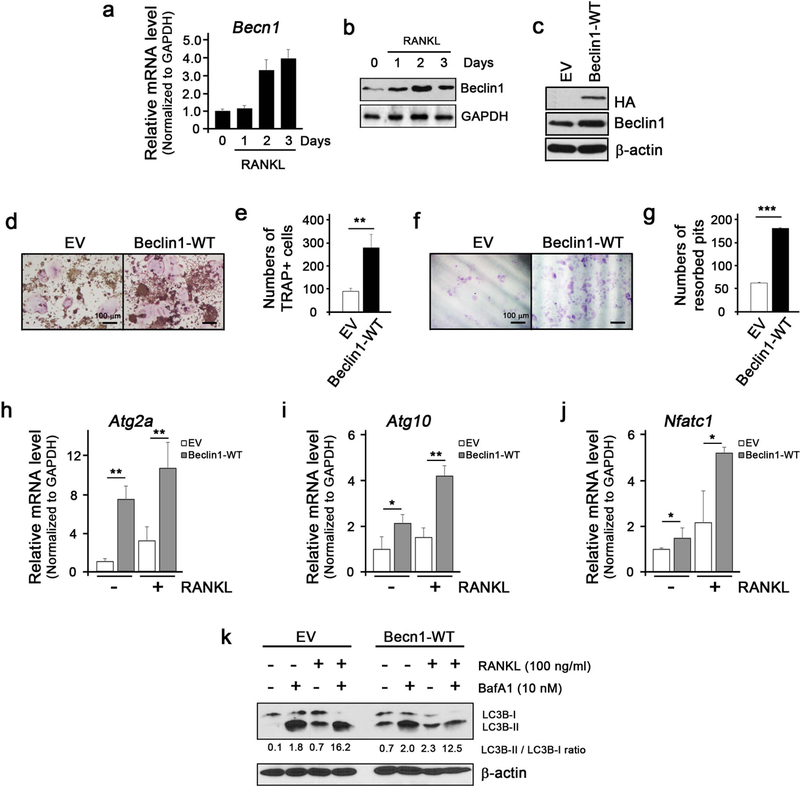
(a) Real-time qPCR for expression of Becn1 mRNA during RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation in RAW 264.7 cells. (b) Western blotting against Beclin1 and GAPDH during RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation in RAW 264.7 cells. (c) Western blotting against HA, Beclin1, and β-actin in RAW 264.7 cells infected with retroviruses harboring empty vector (EV) or wildtype Beclin1 (Beclin1-WT). (d) TRAP staining following RANKL treatment on RAW 264.7 cells for 3 days. Bar = 100 μm. (e) Quantification of TRAP+ cells. (f) Dentin slice assay following RANKL treatment on RAW 264.7 cells for 10 days. Cells were stained with hematoxylin, removed the cells with cotton swabs, and examined under the light microscope. Bar = 100 μm. (g) Quantification of resorbed pits. (h,i,j) Real-time qPCR for expression of Atg2a, Atg10, and Nfatc1 in EV- or Beclin1-WT-expressing RAW 264.7 cells treated with RANKL. (k) Western blotting against LC3B and β-actin during RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation in RAW 264.7 cells with or without BafA1.
