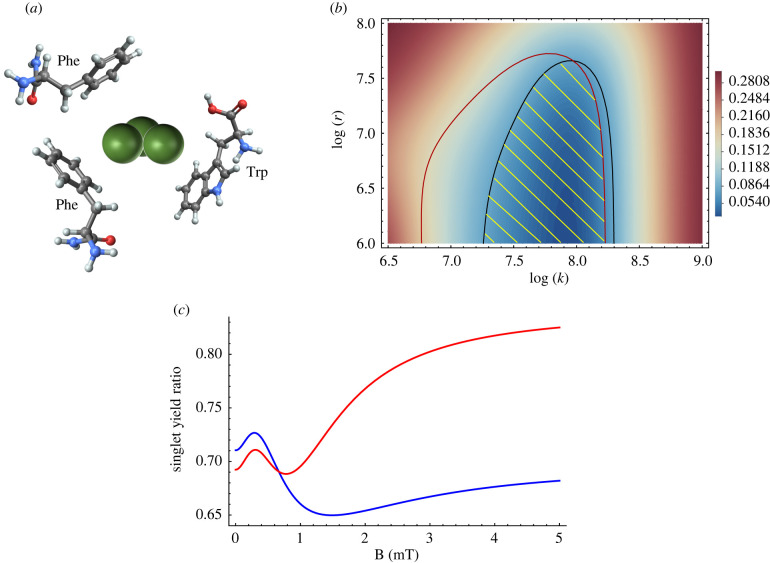
Figure 4.
Radical pair explanation for isotope effects in xenon-induced anaesthesia. (a) Schematic presentation of the interaction of xenon (green spheres) with aromatic rings of tryptophan (Trp) and phenylalanine (Phe) at the glycine-binding site of the NMDAR [483]. (b) The dependence of the agreement between relative anaesthetic potency and singlet yield ratio on the relationship between relaxation rate, r, and reaction rate, k. The radical pair model can explain the experimentally derived relative anaesthetic potency of xenon, shaded in yellow. (c) Predicted dependence of the anaesthetic potency as given by the singlet yield ratio, based on the radical pair model of 129Xe/130Xe (blue) and 131Xe/130Xe (red) on an external magnetic field [57].