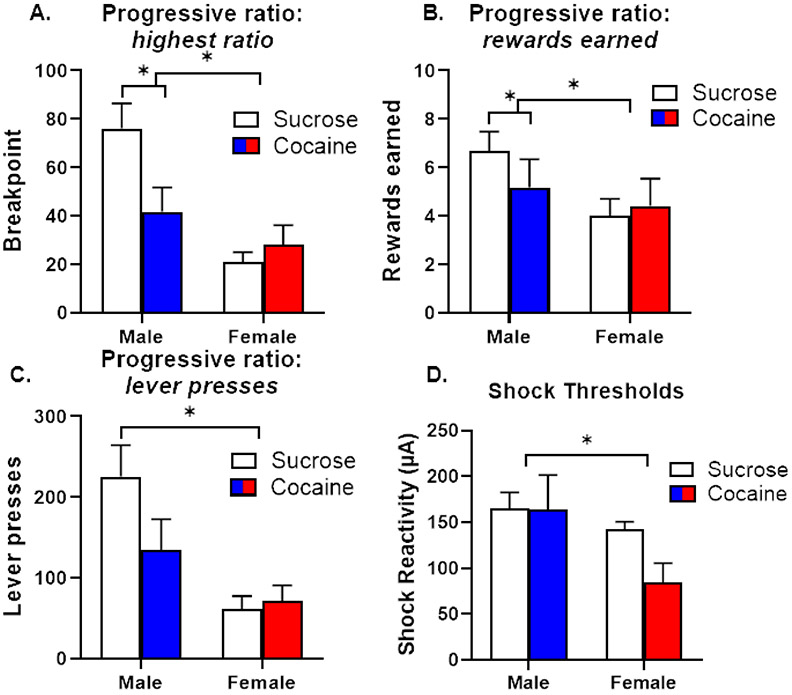
Figure 4. Performance on behavioral assays of food motivation and shock reactivity (Experiment 2).
A. Male rats that underwent sucrose self-administration reached a significantly higher breakpoint on a progressive ratio (PR) schedule of reinforcement than male rats that underwent cocaine self-administration. There were no differences in breakpoint between female self-administration groups. B. Male rats that underwent sucrose self-administration earned significantly more food rewards on the PR assay than male rats that underwent cocaine self-administration. There were no differences in the number of rewards earned between female self-administration groups. C. Male rats made significantly more lever presses for rewards than female rats. D. Shock thresholds were significantly higher in males than females, irrespective of self-administration group. Data are represented as mean ± standard error of the mean. Asterisks denote p < 0.05.