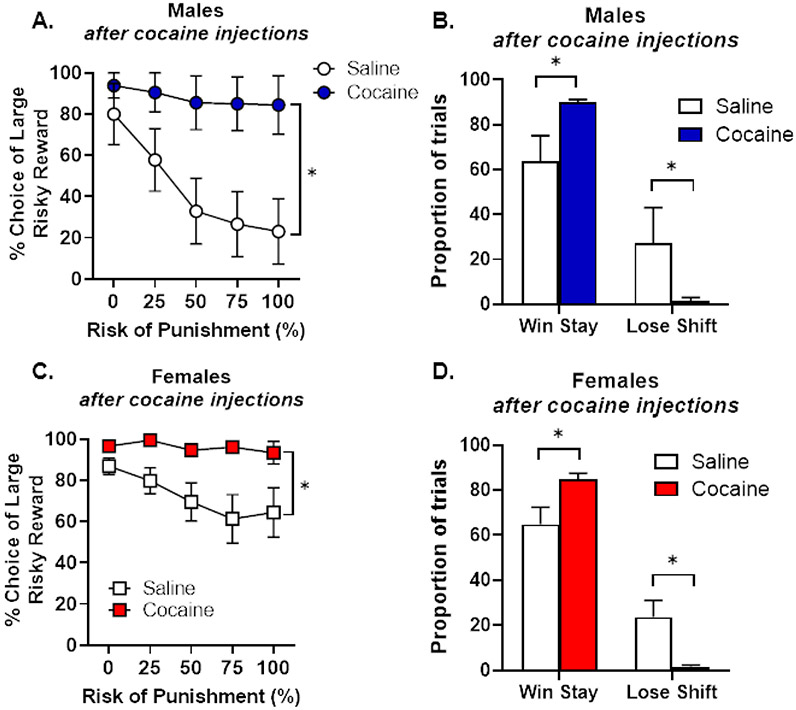
Figure 7. Performance in the Risky Decision-making Task after passively administered cocaine (Experiment 4).
A. Male rats that received cocaine injections chose the large, risky reward significantly more than rats that received control saline injections. B. Male rats that received cocaine injections displayed an increase in win-stay behavior and a decrease in lose-shift behavior relative to male rats that received saline injections. C. Female rats that received cocaine injections chose the large, risky reward significantly more than rats that received control saline injections. D. Female rats that received cocaine injections displayed an increase in win-stay behavior and a decrease in lose-shift behavior relative to female rats that received saline injections. Data are represented as mean ± standard error of the mean. Asterisks denote p < 0.05.