Figure EV4. PPARα deletion increases ferroptosis caused by iron overload.
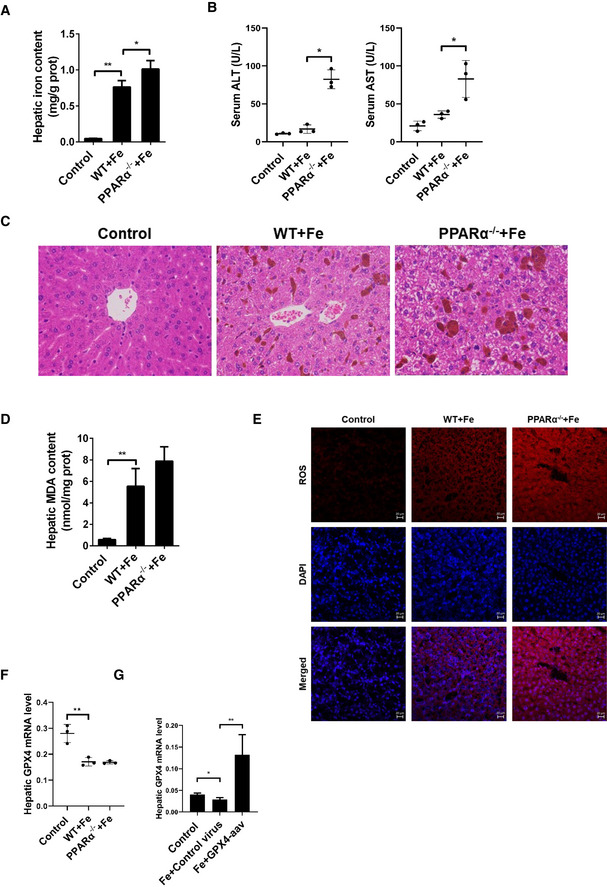
- Hepatic iron content was measured in 8‐week‐old WT, PPARα−/− mice that received intraperitoneal injections of dextriferron or saline.
- Serum ALT and AST levels was measured in 8‐week‐old WT, PPARα−/− mice that received intraperitoneal injections of dextriferron or saline.
- Liver sections were obtained from the indicated mice and stained with H&E. All scale bars are 50 μm. n = 3 biological replicates.
- Hepatic MDA content was measured in 8‐week‐old WT, PPARα−/− mice that received intraperitoneal injections of dextriferron or saline.
- Measurement of intracellular ROS levels by fluorescent probe DCFH‐DA, and the fluorescence intensity of ROS was calculated. All scale bars are 20 μm. n = 3 biological replicates.
- Hepatic Gpx4 mRNA levels were measured in the indicated mice.
- Hepatic Gpx4 mRNA levels were measured in the mice that were fed a HID with or without Gpx4‐AAV treatment.
Data information: In (A–G), n = 3–5 mice/group. mRNA levels were normalized to 36B4 and are expressed relative to the mean value of the WT group; Data are presented as means ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, determined by ANOVA.
