Figure 7. Hypothetical model for the mechanism of MTAP‐mediated suppression of lung cancer metastasis.
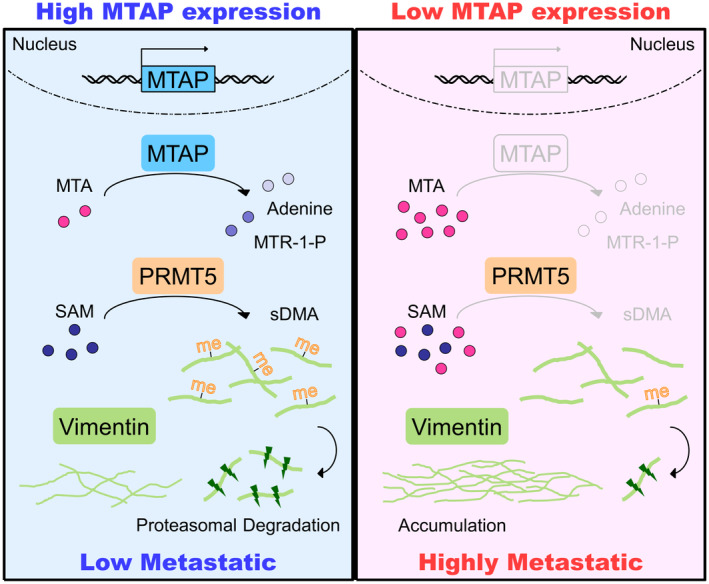
Our invasion cell‐based model demonstrated that in high MTAP‐expressing low metastatic cancer cells, MTA level is relatively low, facilitating PRMT5 to dimethylate vimentin, leading to vimentin degradation. Conversely, in highly metastatic cancer cells with MTAP loss, accumulated MTA inhibits PRMT5 activity so that low dimethylated vimentin is stabilized and responsible for lung cancer metastasis.
