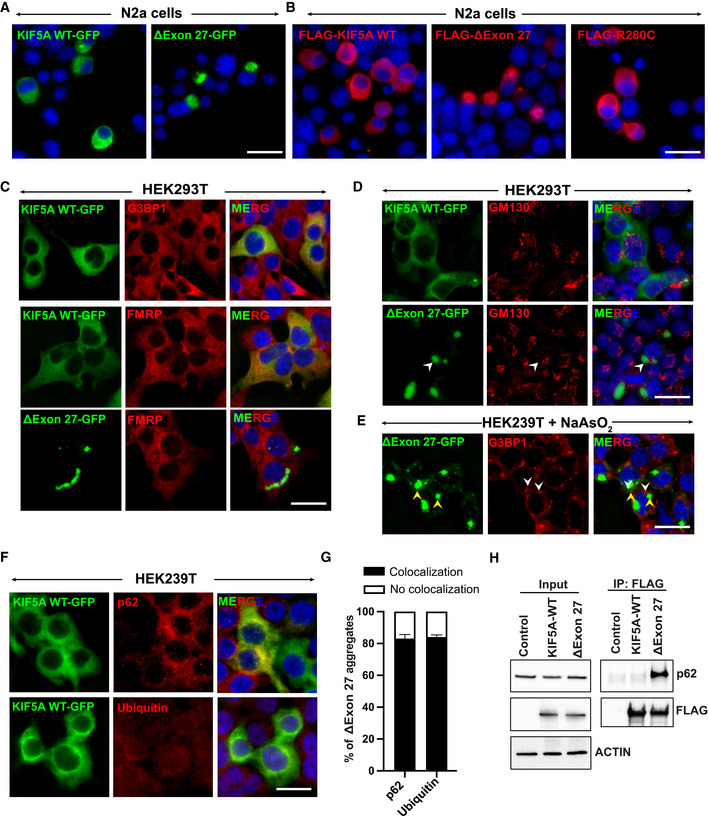
-
A, B
Expression of human KIF5A WT and disease‐associated mutants with C‐terminal GFP (A) or N‐terminal FLAG (B) tags in N2a cells. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
C
Colocalization of G3BP1 and FMRP, markers of stress granules, with KIF5A WT or ∆Exon27 expressed in HEK293T cells. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
D
GM130 (a Golgi marker) staining in HEK293T cells expressing either KIF5A WT or ∆Exon27. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
E
G3BP1 staining in HEK239T cells expressing ∆Exon27 and treated with sodium arsenite (200 μM) for 30 min. White and yellow arrowheads highlight stress granules and ∆Exon27 aggregates respectively. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
F
p62 and ubiquitin staining in KIF5A WT expressing HEK293T cells. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
G
Percent of cells with p62 and ubiquitin colocalized with cytoplasmic ∆Exon27 granules. Bars indicate mean ± SD.
-
H
Immunoprecipitation of KIF5A using antibodies against the N‐terminal FLAG tag also pulled down endogenous p62 only in cells expressing Δexon27, but not WT KIF5A. Three biological replicates, n = 200 cells per experiment.