-
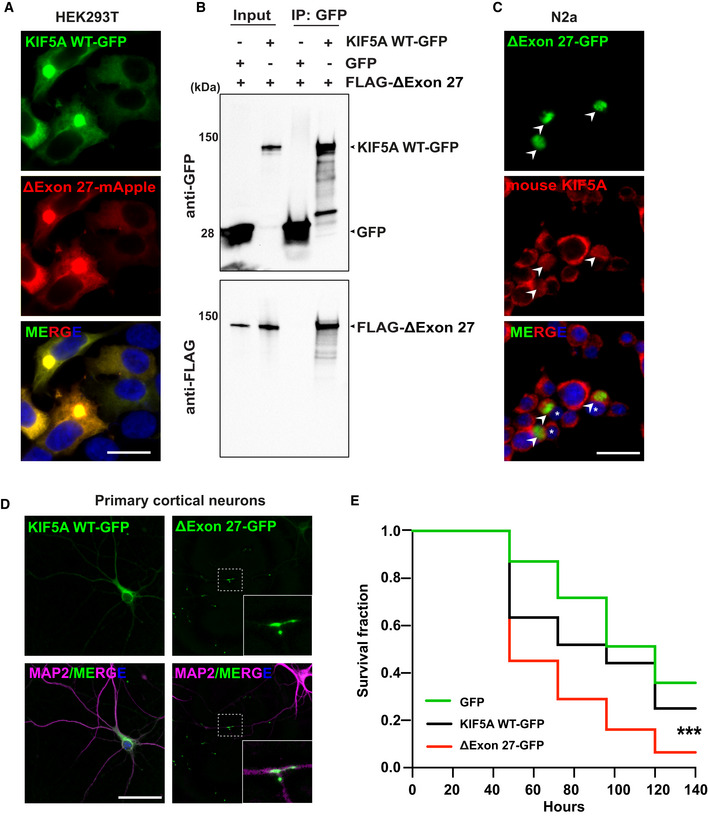
A
Expression of KIF5A WT and ΔExon27 tagged with GFP and mApple, respectively, in HEK293T cells. Images were taken 48 h after transfection, two biological replicates. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
B
Pull‐down analysis showing the association of ΔExon27 with WT KIF5A, two biological replicates.
-
C
Staining of mouse endogenous KIF5A in N2a cells transfected with ΔExon27‐GFP using an antibody generated with a peptide corresponding to the C‐terminus of KIF5A WT (amino acids 1007–1027), which does not recognize ΔExon27. ΔExon27 granules are highlighted with arrowheads. The nuclei of cells expressing ΔExon27 are indicated with asterisk, two biological replicates. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
D
Mouse primary neurons transfected with KIF5A WT‐GFP and ΔExon27‐GFP were probed using anti‐GFP antibody 24 h after transfection. Neurons were identified by microtubule‐associated protein 2 (MAP2) and nuclei were stained with DAPI, three biological replicates, n = 200 cells per experiment. Scale bar: 20 μm.
-
E
Five‐day‐old mouse cortical neurons were transfected with mApple together with either GFP (n = 150), KIF5A WT‐GFP (n = 160), or ΔExon27‐GFP (n = 135), three biological replicates. Images were taken every 24 h after transfection. Survival of neurons was analyzed by Kaplan–Meier survival analysis (***P < 0.0001, log‐rank test).