-
A
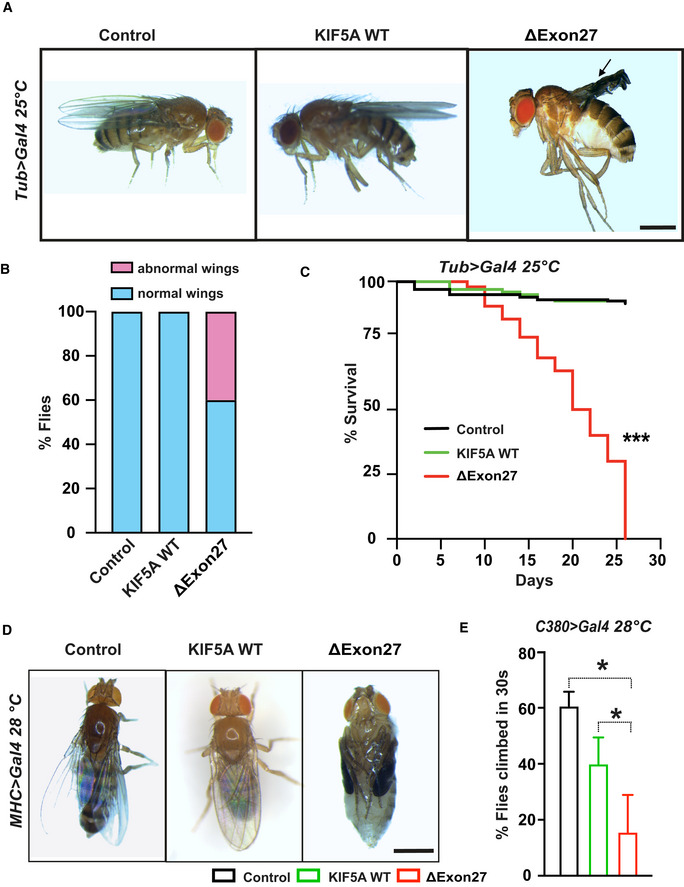
Ubiquitous overexpression of ΔExon27 leads to wing defects (black arrows). Scale bar: 0.5 mm.
-
B
Percent of flies with normal and abnormal wings (n = 50 flies per group, two independent experiments).
-
C
Life spans were analyzed for flies expressing KIF5A WT‐GFP and ∆Exon27‐GFP, and control flies expressing tubulin‐Gal4 only. Expression of ∆Exon27‐GFP by the tubulin driver causes a substantial decrease in viability (***P < 0.001, log‐rank test), n = 50 flies per group, two independent experiments.
-
D
Expression of ∆Exon27‐GFP in Drosophila muscles leads to complete paralysis. The pupal case of the fly expressing ∆Exon27‐GFP has been removed for this picture. The folded wings and legs are characteristic of the pupal state in flies expressing ∆Exon27. Scale bar: 0.5 mm.
-
E
Negative geotaxis assay showing reduced motor function in 25‐day‐old flies expressing ∆Exon27‐GFP driven by a motor neuron‐specific driver (C380‐Gal4; n = 50 flies each group, two independent experiments). Bars indicate mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using one‐way ANOVA (*P < 0.05).