Figure 6. Proposed mechanisms of neuronal toxicity caused by KIF5A ∆Exon27 gain‐of‐function.
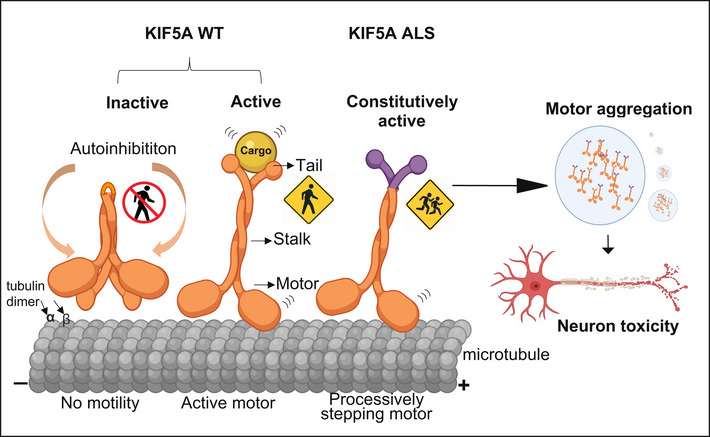
In the absence of tethered cargos, KIF5A WT is autoinhibited with the C‐terminal tail binding to the N‐terminal motor domain. When cargo binds to the C‐terminal tail, the motor associates with microtubules and starts a processive run toward the plus‐ends. ALS‐associated KIF5A ∆Exon27 with the aberrant C‐terminal tail relieves from the “autoinhibited” state even without cargo and self‐associates to form multiple motors, leading to a drastically increased run‐length on microtubules and accumulation at the plus‐ends. ∆Exon27 also forms complexes with WT KIF5A and enhances motor self‐association and aggregation. The image was created at BioRender.com.
