Fig. 1.
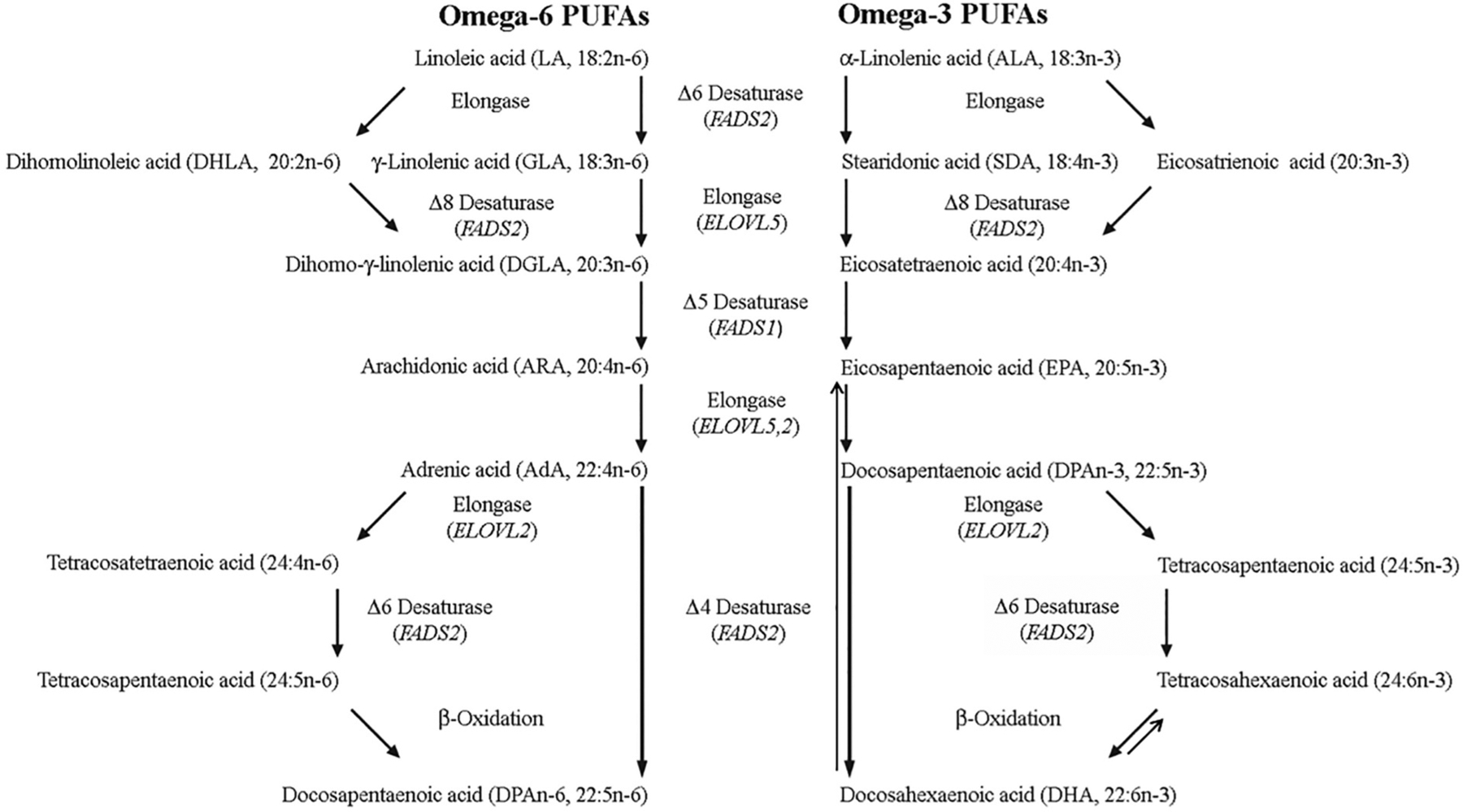
Biosynthesis of omega-3 and omega-6 PUFAs. The biosynthesis of longer-chain omega-3 and omega-6 PUFAs proceeds via a series of alternating position-specific desaturation and elongation steps from ALA and LA, respectively. FADS1 and FADS2 appear responsible for all omega-3 and omega-6 PUFA desaturation in mammals, with FADS1 exhibiting Δ5-desaturase activity, and although FADS2 was originally identified as the Δ6-desaturase, it has subsequently been shown to also possess Δ4- and Δ8-desaturase activities. Octadecanoids are lipid mediators derived from C18 PUFAs, such as ALA or LA, eicosanoids are derived from C20 PUFAs such as DGLA, ARA or EPA, and docosanoids are derived from C22 PUFAs such as DPAn-3, and DHA. See text for further details.
