Fig. 3.
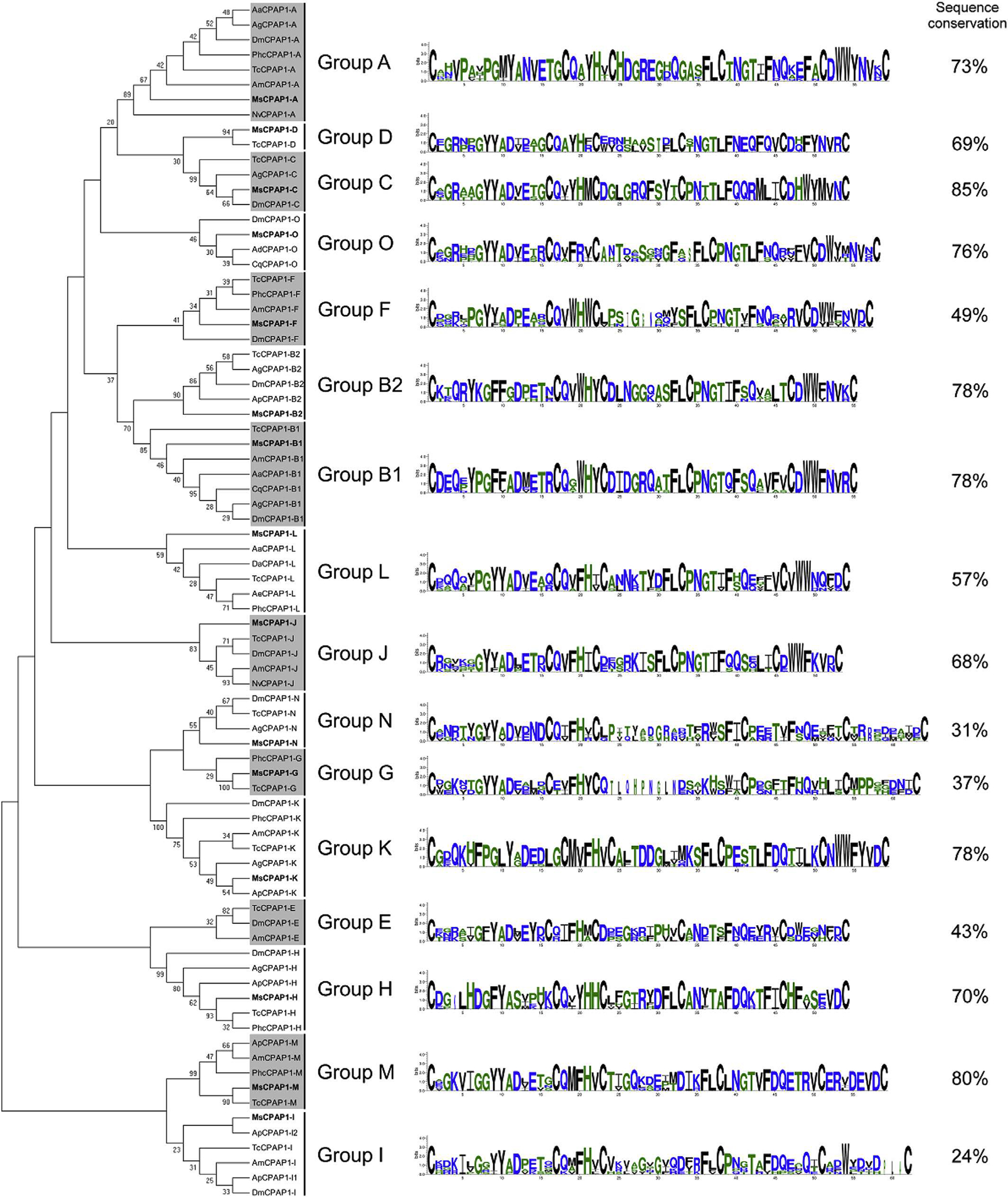
Phylogenetic analysis of the chitin-binding domain of CPAP1s from thirteen different insect species; Acromyrmex echinatior (Ae), Acyrthosiphon pisum (Ap), Aedes aegypti (Aa), Anopheles darling (Ad), Anopheles gambiae (Ag), Apis mellifem (Am), Culex quinquefasciatus (Cq), Drosophila ananassae (Da), Drosophila melanogaster (Dm), M. sexto (Ms), Nasonia vitripennis (Np), Pedicuius humanus corporis (Phc), Tribolium castaneum (Tc). The accession numbers of all the proteins used are listed in Supplementary Table 1. CPAP1 s from M. sexta are indicated in bold. CPAP1s are grouped into sixteen different groups; the sequence logos of the chitin-binding domain and the percentage of sequence conservation (identical amino adds between all sequences) are shown on the right for each group.
