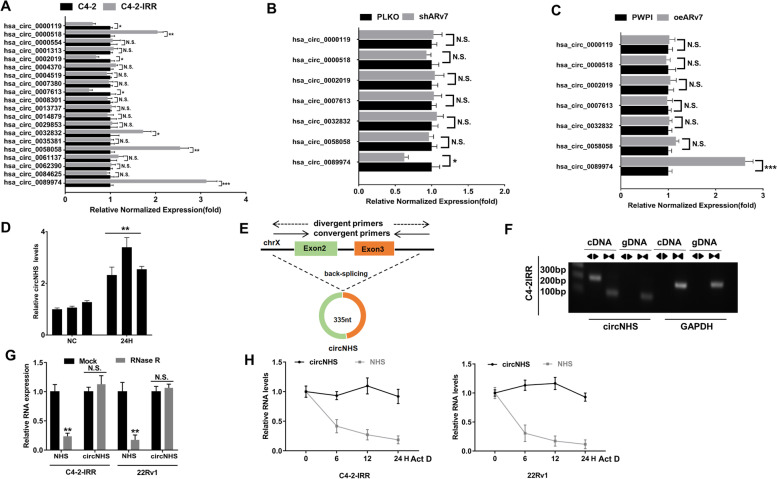
Fig. 2.
A PCR analysis of 20 circRNAs levels in C4-2 parental cells and C4-2-IRR cells. B Knocking down ARv7 with shARv7 in C4-2-IRR cells and PCR analysis of 7 circRNAs levels. C oeARv7 in C4-2 parental cells and PCR analysis of 7 circRNAs levels. D circNHS levels in 22Rv1 cells xenografts after 4 Gy IR treatment. E Schematic diagram of the genomic location and splicing pattern of circNHS. F The existence of circNHS was validated in C4-2 parental cells and 22Rv1 cells by PCR. Divergent primers amplified circNHS from cDNA, but not from genomic DNA (gDNA). GAPDH was used as a negative control. G PCR analysis of RNase R treatment assay to confirm the circNHS formation is a circRNA sequence. H The relative RNA levels of circNHS and NHS were analyzed by RT-qPCR after treatment with Actinomycin D at the indicated time points. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the controls. N.S., not significant