FIGURE 3.
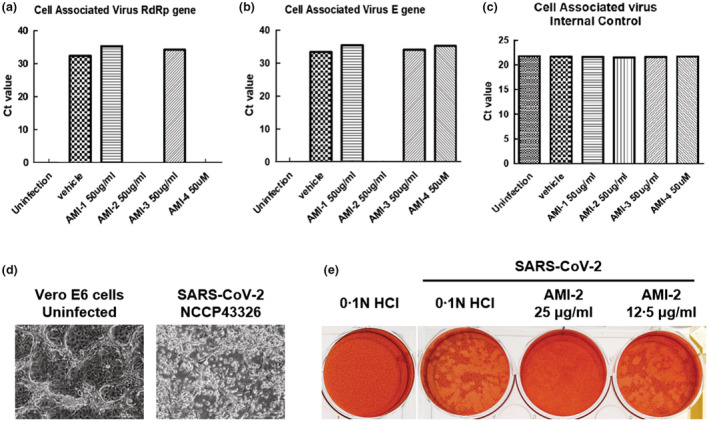
Effects of chitosan‐based substances on SARS‐CoV‐2. (a–c) Antiviral effect of chitosan‐based substances on SARS‐CoV‐2 through qPCR analysis. The amount of SARS‐CoV‐2 virus at MOI 0.01 was incubated with 50 μg/ml of chitosan‐based substances (AMI‐1, −2, and −3) or 50 μM of AMI‐4 for 1 h at room temperature, infected with Vero E6 cells, and incubated with the substances for 48 h. Viral RNA was extracted from the culture medium of the cells, and the SARS‐CoV‐2 gene was detected through qPCR analysis. The graph of Ct value was represented to (a) RNA‐dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) gene, (b) envelope (E) gene of SARS‐CoV‐2 and (c) internal control of qPCR kits, respectively. (d) The cytopathic effect of SARS‐CoV‐2 on Vero E6 cells. The images of cytopathic effects of Vero E6 cells infected with SARS‐CoV‐2 (NCCP43326) for 4 days were obtained by phase‐contrast microscopy images. Representative single optical sections are shown. Scale bars, 100 μm. (e) Plaque assay of SARS‐CoV‐2 infected Vero E6 cells. After 1 h of the virus within indicated concentration of AMI‐2 adsorption, low‐melting agar containing first overlays were added. Secondary overlays were added after 5 days, and the cells were incubated overnight. Use a white‐light transilluminator (light box) to aid in visualize the plaques.
