FIGURE 6.
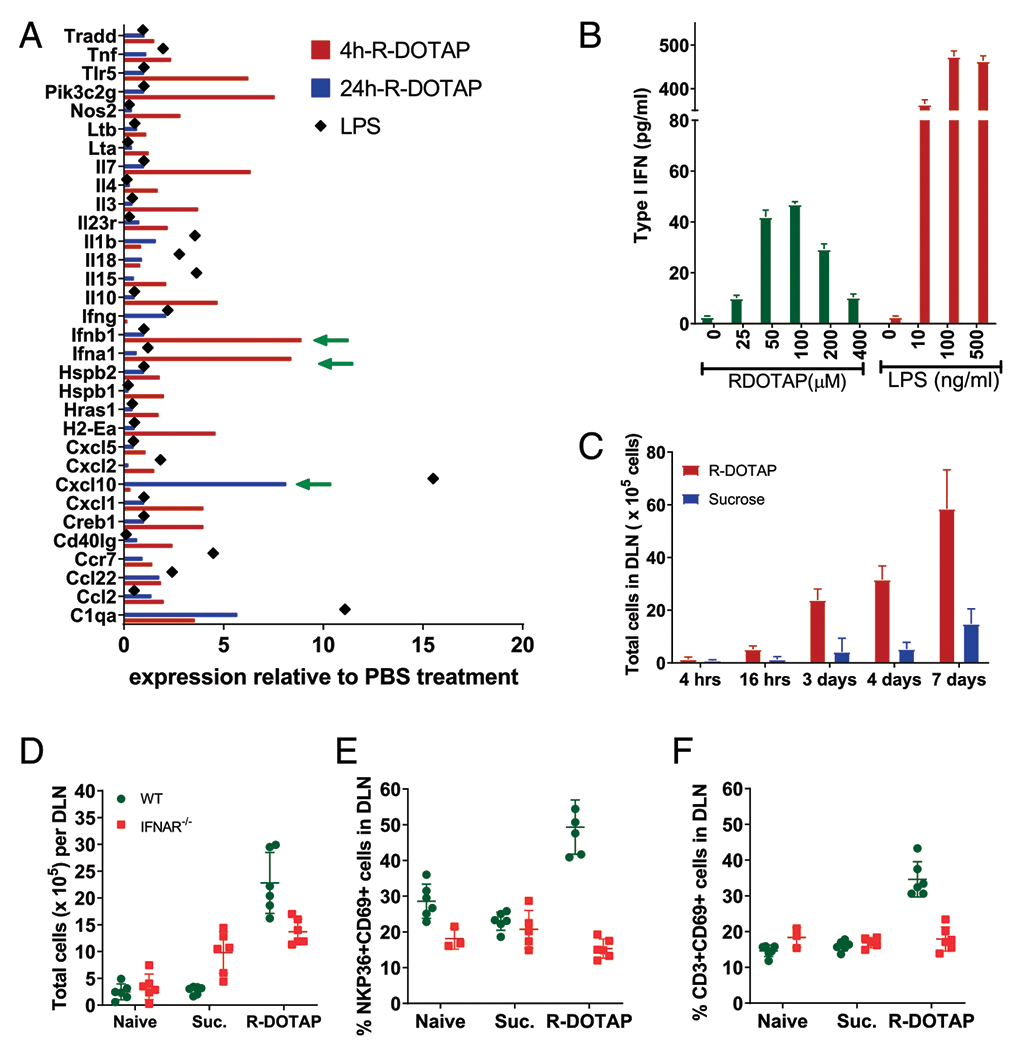
R-DOTAP administration induces production of type I IFN in the DLN in vivo. (A) Groups of four C57BL/6 mice were injected with R-DOTAP, PBS, or LPS at the nape of the neck, and draining axillary and brachial LNs were harvested from each mouse after 4 or 24 h. CD11c+ cells from pooled LNs of each individual mouse were sort-purified, and relative gene expression was analyzed using Nanostring technology. Shown are mean RNA expression levels for genes from the R-DOTAP or LPS groups that showed >0.5-fold difference relative to PBS treatment. (B) BMDCs from IFNAR−/− mice were stimulated with the indicated concentrations of R-DOTAP nanoparticles or LPS for 24 h, and type I IFN production was measured using an IFN-α/β reporter assay. (C) Mice were injected with R-DOTAP or sucrose in the footpad, DLN were harvested at the indicated times and enzymatically digested, and total cell number was enumerated. (D) Wild-type (WT) or IFNAR−/− mice were administered R-DOTAP or sucrose (Suc.) in the footpad, and total cells per DLN were quantitated after 24 h. (E) DLN from mice described in (D) were analyzed for the percentage of CD69+ NKP36+ NK cells or (F) the percent of CD69+ CD3+ T cells. Experiments were repeated at least three times with similar results.
