Figure 1.
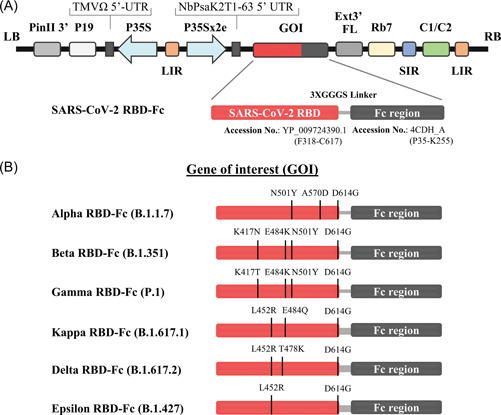
Schematic representation of geminiviral vector (pBY2eK) map of SARS‐CoV‐2 variant RBD‐Fc fusion proteins produced in N. benthamiana. T‐DNA region between LB (left border) and RB (right border) of pBY2eK consists of PinII 3′ (terminator from potato proteinase inhibitor II gene), P19 (P19 gene from tomato bushy stunt virus (TBSV)), TMVΩ 5′‐UTR (5′ untranslated region of tobacco mosaic virus Ω), P35S (cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter), LIR (long intergenic region of BeYDV genome), NbPsaK2T 5′UTR (5′ untranslated region), GOI (gene of interest), Ext3′FL (3′ full length of the tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) extension gene), Rb7 (tobacco RB7 promoter), SIR (short intergenic region of BeYDV genome), and C2/C1 (bean yellow dwarf virus (BeYDV) open reading frames C1 and C2 encoding for replication initiation protein (Rep) and RepA) (A). Diagrammatic representation of the SARS‐CoV‐2 variant RBD‐Fc fusion proteins. The RBD protein with the predicted mutation sites in the SARS‐CoV‐2 variants compared to the RBD of original strain Wuhan was highlighted (B). RBD, receptor‐binding domain; SARS‐CoV‐2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
