Figure 1.
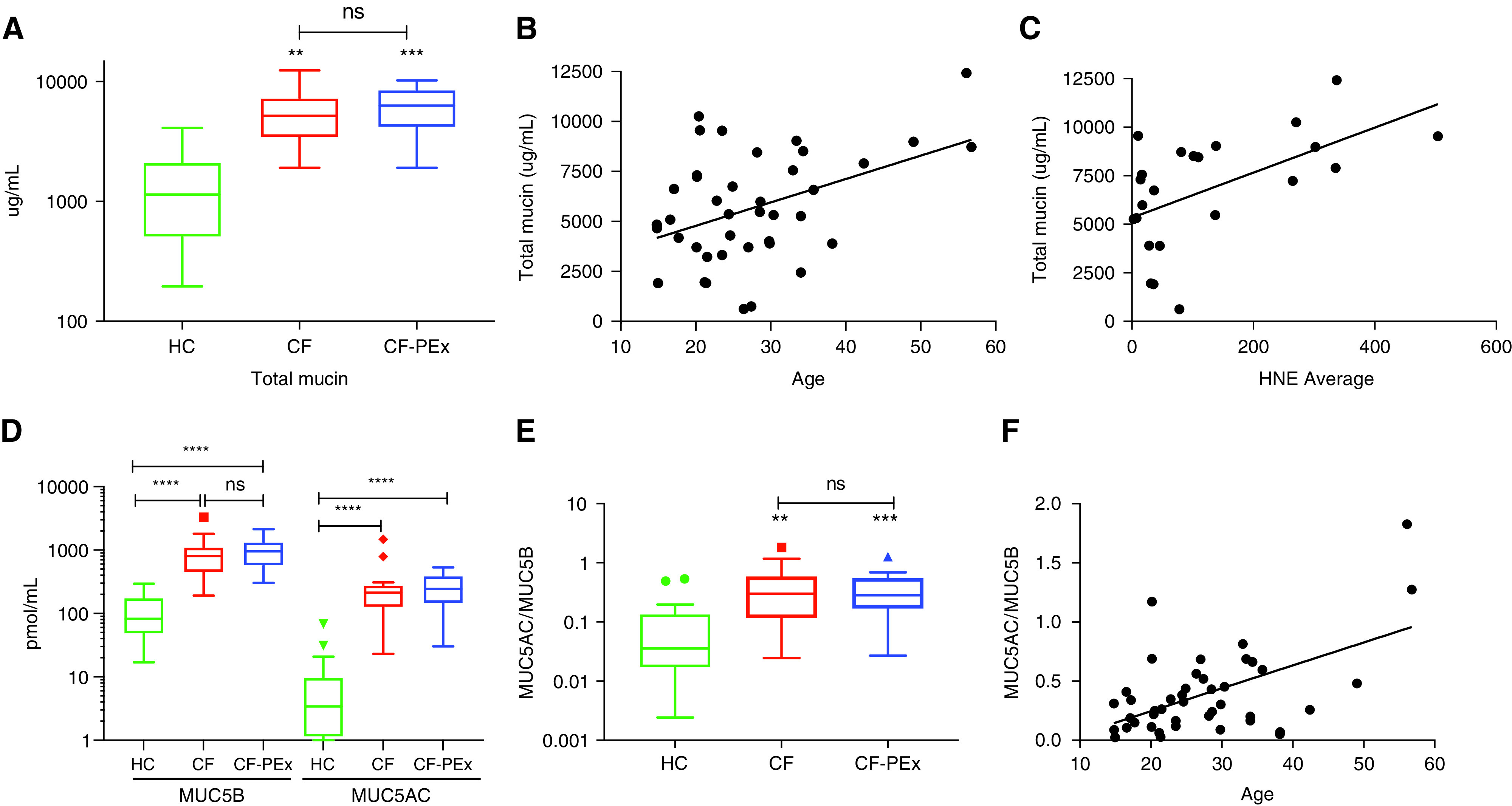
Mucin concentration increases significantly in cystic fibrosis (CF). (A) Total mucin concentrations of CF sputum is significantly higher than healthy control (HC) but does not differ between stable CF and CF with pulmonary exacerbation (CF-PEx) disease status. (B and C) Correlation between total mucin concentration and age (B) (n = 40) (Pearson r = 0.430; P = 0.006) and HNE (C) (n = 23) (Pearson r = 0.552; P = 0.006). (D and E) Absolute MUC5B and MUC5AC concentrations and the MUC5AC/MUC5B ratio are significantly elevated in CF but do not differ between stable and exacerbation disease status (healthy, n = 19; CF stable, n = 17; and CF exacerbation, n = 24). (F) Correlation of the ratio of MUC5AC/MUC5B ratio and age (n = 43) (Pearson r = 0.546; P = 0.00015). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005, and ****P < 0.001. FEV1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 second; HNE = human neutrophil elastase; ns = not significant.
