Fig. 3.
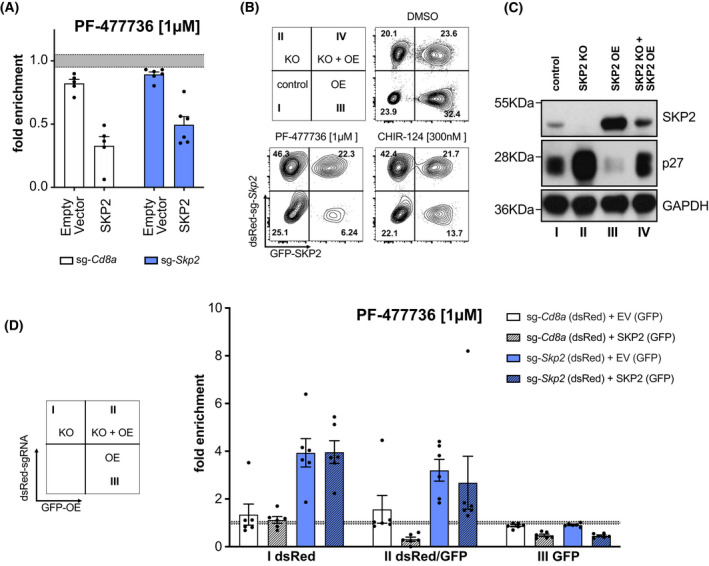
Exogenous SKP2 restores sensitivity to CHK1 inhibitors. (A) Baf3 SKP2 KO and sgCd8a control clones (dsRed+) were transduced with human SKP2 or an empty vector (EV), which both express GFP as a marker. Three days post transduction cultures were treated with the CHK1i PF‐477736 [1 μm] or DMSO for 48 h. The percentage of GFP+dsRed+ cells was assessed using flow cytometry. Treatments were normalized to the DMSO‐treated controls. Bars indicate the mean fold enrichment (±SEM) of two individual clones per genotype noted in three independent experiments (Cd8a‐1, Skp2‐1, Skp2‐2) and two independent experiments (Cd8a‐2). (B) Representative contour plots of parental cells mixed with SKP2 KO for rescue experiment, depicting the distribution of the four subpopulations (I–IV), with and without treatment of CHK1i after 48 h. Three independent experiments were performed (C) Western blot showing SKP2 and p27 levels of the respective, sorted subpopulations shown in C (DMSO treatment). A single experiment was performed. (D) Quantification of sg‐Skp2/dsRed or sg‐Cd8a/dsRed transduced cells reconstituted with human SKP2 (GFP) or EV (GFP) after 48 h of treatment. The PF‐477736 treated cells were normalized to the DMSO‐treated cells. Bars indicate the mean fold enrichment (±SEM) of two independent sgRNAs (targeting Cd8a or Skp2) in three independent experiments.
