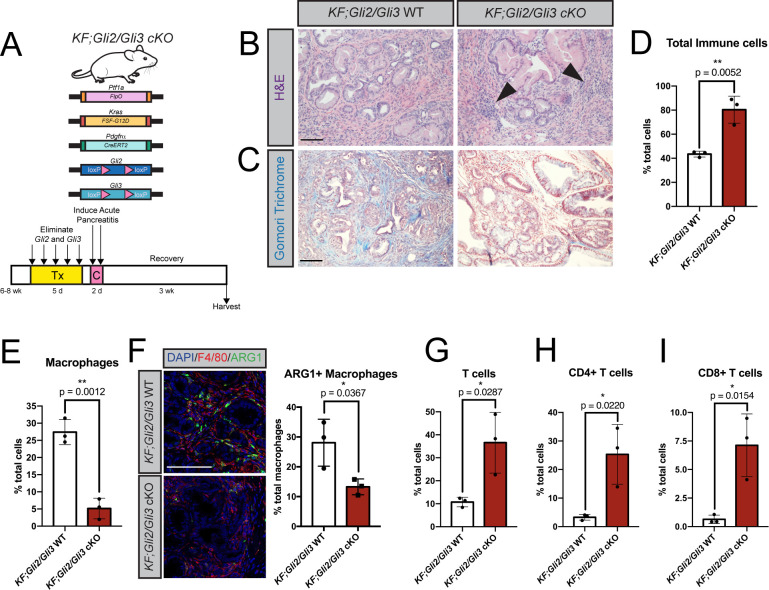
Fig 2. Conditional Gli2 and Gli3 deletion in vivo restricts immunosuppressive macrophages and promotes T cell infiltration.
A) Cartoon depicting experimental strategy. Adult KF; PdgfrαCreERt2/+; Gli2fl/fl; Gli3fl/fl (KF;Gli2/Gli3 cKO) mice were given tamoxifen (Tx, 200mg/kg) once a day for 5 days. Mice were then given 8 hourly injections of caerulein (C) over 2 days to induce pancreatitis. Pancreata were harvested 3 weeks later. B-C) H&E (B) and Gomori trichrome (C) staining of KF;Gli2/Gli3 cKO mice (right) and KF; Gli2fl/fl; Gli3fl/fl (KF;Gli2/Gli3 WT) mice (left). Arrowheads indicate dense pockets of stromal cells. D-E) Flow cytometry analysis of total immune cells (D) and macrophages (E) in KF;Gli2/Gli3 WT and KF;Gli2/Gli3 cKO mice. F) Immunofluorescent antibody detection (left) and quantitation (right) of macrophages (F4/80, red) expressing arginase 1 (ARG1, green). DAPI staining in blue. G-I) Flow cytometry analysis of total T cells (G), CD4+ T cells (H), and CD8+ T Cells (I). N ≥ 3 for all genotypes. All P-values were determined by un-paired t-test. Scale bars = 100μm. Mouse drawing acquired from the open source repository SciDraw.io (doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3925901).