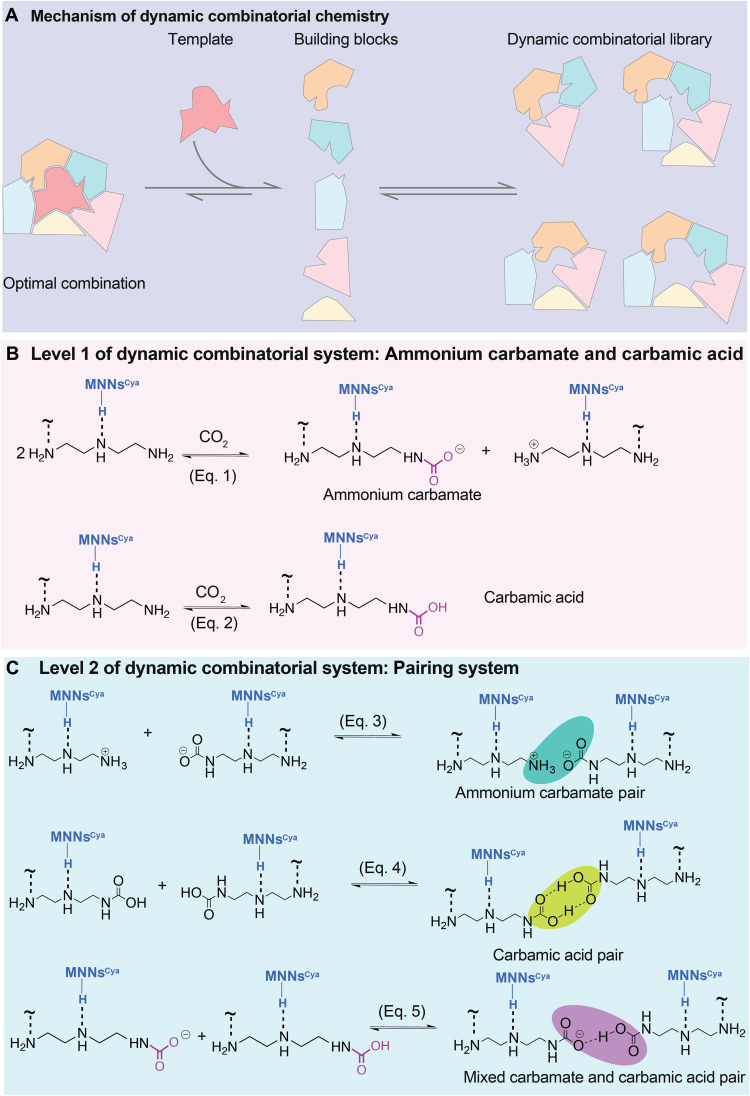
Fig. 3. Five hypothetical CO2 chemisorption mechanisms in MNNsCya ⊃ DETA using a double-level dynamic combinatorial system.
(A) Schematic representation of the fundamental mechanism of DCC. (B) Level 1: the reversible carbamate N─CO2 reactions form ammonium carbamate and carbamic acid (eqs. 1 and 2). (C) Level 2: further pairing formation. Bridge formation between oppositely charged (NH3+ and COO−) species produces ammonium carbamate pairs (eq. 3). Two carbamic acid species can readily form carbamic acid pairs (eq. 4). The mixed ammonium carbamate and carbamic acid adducts give rise to a hydrogen-bonded structure (eq. 5, charge compensating ammonium group not shown on either side of this equation). H is not shown in eq. 5.