Figure 7.
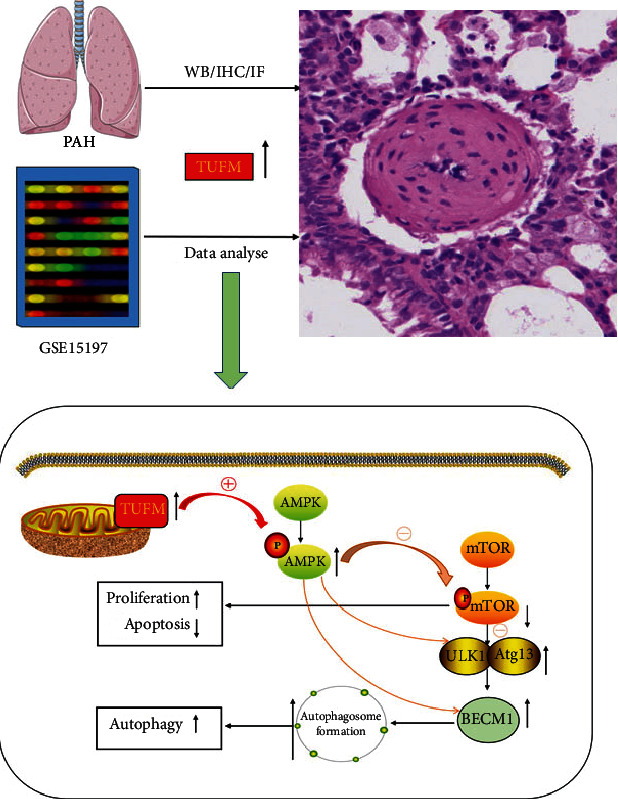
Schematic figure of the current study. Increased TUFM expression in hypoxia-stimulated pulmonary arterial hypertension cells causes an increasing mtDNA translation, leading to dysfunction of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Mitochondrial dysfunction induces cellular stress and then activates AMPK. On the one hand, activated AMPK decreases the phosphorylation level of mTOR, inhibits the activity of mTOR, and then disassociates from ULK1. Thus, phosphorylation of specific sites of ULK1 and Atg13 is released. Meanwhile, the ULK1 complex is activated through autophosphorylation at thr180 and phosphorylates Atg13, FIP200, atg101, and other Atg proteins. The activated ULK1 complex then translocates to the isolation membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, where autophagy is initiated. On the other hand, activated AMPK will directly stimulate ULK1 and BECN1, initiating autophagy.
