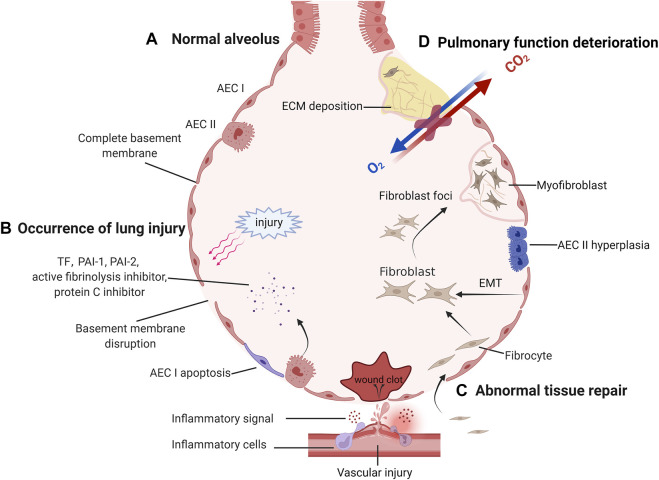
FIGURE 1.
The pathological process of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. (A) After normal alveoli are damaged and abnormally repaired, irreversible lung function deterioration occurs. Normal alveolus has a complete basement membrane and gas exchange function. (B) When the basement membrane continuity is disrupted by external injury, the damaged capillaries and activated AECs release inflammatory signals and coagulation factors, forming a local inflammatory microenvironment. (C) If the damage persists, abnormal repair will be initiated. Lung mesenchymal progenitors, fibrocytes recruited to the lung, and endothelial cells undergoing EMT can aggregate to form fibroblasts foci and differentiate into matrix-secreting myofibroblasts. To compensate for the local blood supply to the alveoli, new blood vessels are gradually formed. (D) As fibroblast foci increased, more ECM was deposited and cross-linked together, triggering a deterioration in lung compliance and gas exchange function.