Figure 1.
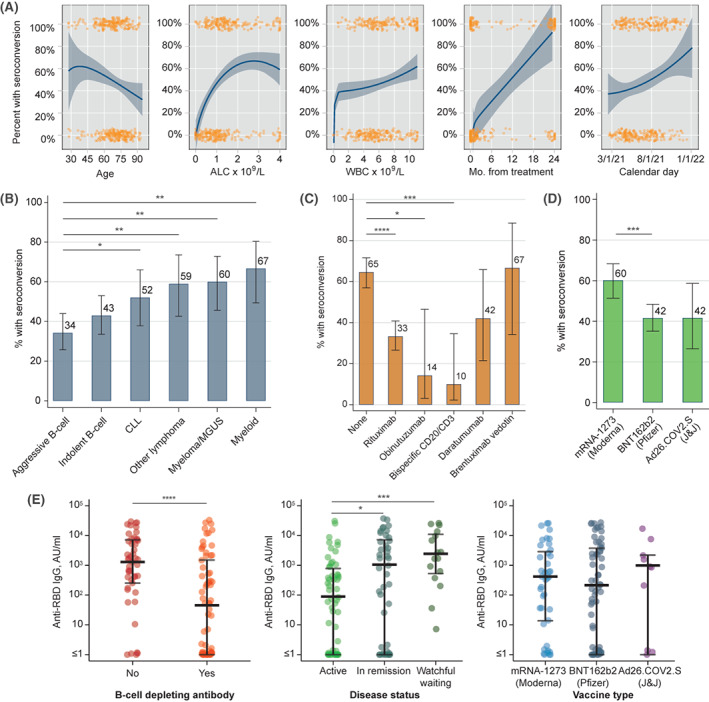
Association between seroconversion after initial COVID‐19 vaccination and (A) continuous variables, (B) type of hematologic malignancy, (C) prior exposure to specific monoclonal antibodies (only agents with n > 10 shown), and (D) specific COVID‐19 vaccine. (E) Levels of anti‐RBD IgG antibody after the initial vaccination according to prior exposure to B‐cell–depleting antibody, disease status, and type of initial vaccine. Variables in A include: age, absolute lymphocyte count (ALC) (capped at the upper limit of normal 4 × 10 9 /L), white blood cell count (WBC) (capped at upper limit of normal 11 × 10 9 /L), months (Mo.) from last disease‐directed therapy, and calendar month in 2021; orange markers indicate each individual data point, lines and shaded areas indicate fractional polynomial fit with 95% confidence interval. Asterisks in B–E indicate statistical significance on univariate testing: *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001, ****p < .0001. Ad26.COV2.S indicates adenovirus serotype 26 against the severe acute respiratory‐coronavirus 2 spike protein; anti‐RBD IgG, immunoglobulin G against receptor‐binding domain; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; COVID‐19, coronavirus disease 2019; J&J, Johnson & Johnson; MGUS, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance; mRNA, messenger RNA.
