FIGURE 4.
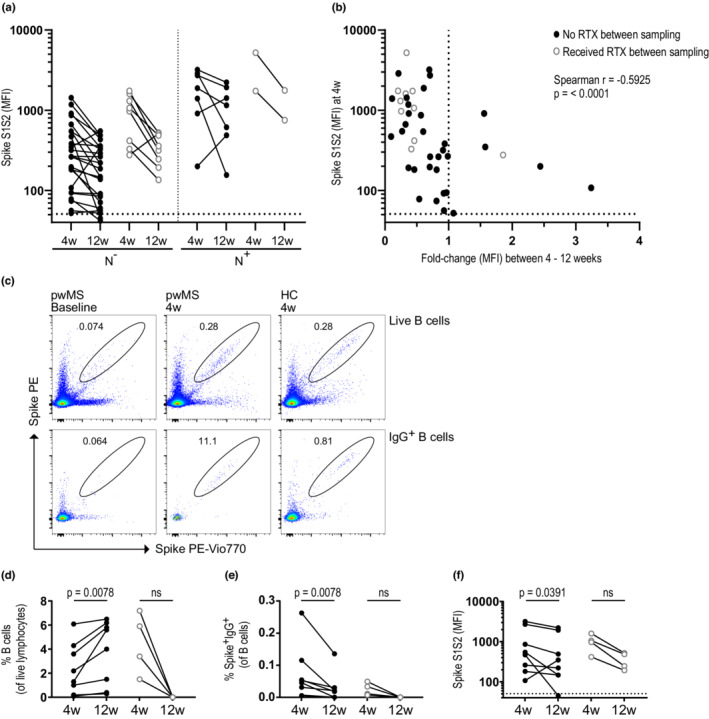
Rituximab (RTX) treatment between 4 (4w) and 12 weeks (12w) postvaccination does not impact SARS‐CoV‐2‐specific antibody levels. (a) Spike S1S2 antibody levels among seroconverted persons with multiple sclerosis (pwMS) on anti‐CD20 between 4 and 12 weeks after booster. Individuals with a likely previous COVID‐19 infection (N+) were separated from naïvely vaccinated (N−) subjects as in b. Further subdivision is shown between individuals who received treatment between the sample time points (open gray circles; n [N−] = 8, n [N+] = 2) and those who did not receive treatment (black circles; n [N−] = 25, n [N+] = 7). (b) Correlation between the spike S1S2 antibody levels at 4 weeks and the fold‐change in antibody levels between 4 and 12 weeks after booster in pwMS on anti‐CD20 treatment who were seroconverted at 4 weeks. (c) Representative dot plots for detection of spike‐specific B cells in pwMS and healthy controls (HC) at baseline and 4 weeks after booster. (d, e) Percentages of B cells of live lymphocytes (d) and percentages of spike‐specific IgG+ B cells (e) 4 and 12 weeks after booster in a subset of pwMS on RTX who did not receive (black circles, n = 8) or did receive (open gray circles, n = 4) RTX between these time points. (f) Spike S1S2 antibody levels 4 and 12 weeks after booster in the same pwMS cohort as in d and e. Dots represent individual data points. Dotted lines indicate cutoff value for antibody positivity. Wilcoxon matched‐pairs signed rank test was used for statistical analysis, and p‐values < 0.05 were considered significant. Spearman r and p‐values are shown. MFI, median fluorescent intensity; ns, not significant; PE, phycoerythrin
