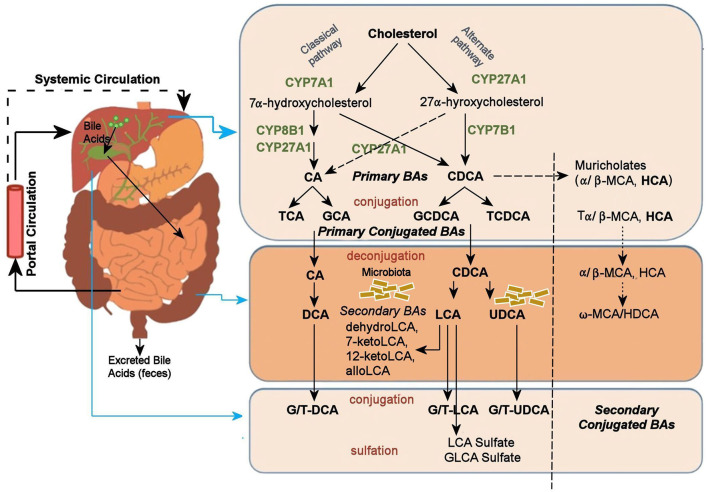
Figure 1.
Bile acid metabolism pathway. Bile acids are synthesized from cholesterol in the liver mainly by two pathways. The classical pathway is initiated by the rate-limiting enzyme, CYP7A1 that synthesizes the two primary bile acids in humans, CA and CDCA. CYP8B1 is required for CA synthesis along with the mitochondrial CYP27A1 that catalyzes a steroid side-chain oxidation. The alternative pathway is initiated by CYP27A1, followed by CYP7B1. After synthesis, the primary bile acids are conjugated to the amino acids taurine or glycine for biliary secretion. In the distal ileum and colon, gut bacteria deconjugates the conjugated bile acids, and bacterial 7α-dehydroxylase removes the 7α-hydroxyl group to convert CA and CDCA to the secondary bile acids DCA and LCA, respectively. The LCA as a high toxic bile acid is mostly excreted by feces. A small amount of LCA, which is recycled back into the liver, is subjected to sulfor conjugation at the 3–hydroxy position of sulfotransferase 2A1 (SULT2A1). Sulfoconjugated BAs are almost never reabsorbed by the most important transport proteins, and they are excreted from the body. Several other bacterial modifications are now known that result in the production of a no of different secondary BAs. The classical pathway is the major pathway for daily synthesis of about 80–90% of the bile acids in humans, whereas the alternative pathway synthesizes about 10–20%. Most bile acids (~95%) are reabsorbed in the ileum and transported via portal blood to the liver to inhibit bile acid synthesis. A small amount of bile acids (~5%) lost in feces is replenished by de novo synthesis. BA, Bile Acid; CA, Cholic Acid; CDCA, Chenodeoxycholic Acid; DCA, Deoxycholic Acid; FXR, Farnesoid X Receptor; GCA, Glycocholic Acid; GCDCA, Glycochenodeoxycholic Acid; GLCA, Glycolithocholic Acid; HCA, Hydroxycitric Acid; HDCA, Hyodeoxycholic Acid; LCA, Lithocholic Acid; MCA, Monocarboxylic Acid; TCA, Taurocholic Acid; TCDCA, Taurochenodeoxycholic Acid; UDCA, Ursodeoxycholic Acid.