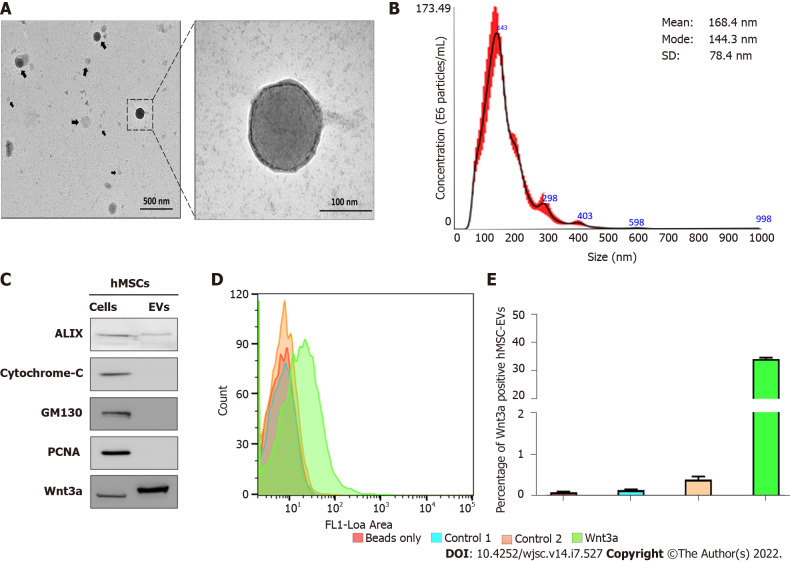
Figure 1.
Isolation and characterization of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. A: The morphology of human mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles (hMSC-EVs) was confirmed using transmission electron microscopy (scale bars: 500 and 100 nm); B: hMSC-EV size was determined using nanoparticle tracking analysis (n = 5); C: Western blot analysis using Alix, cytochrome C, GM130, PCNA, and Wnt3a antibodies on hMSCs and hMSC-EVs; D and E: Flow cytometry count graphs of only beads, control 1 (beads + hMSC-EVs), control 2 [beads + hMSC-EVs + Secondary fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) antibody], and Wnt3a (beads + hMSC-EVs + Wnt3a antibody + Secondary FITC antibody) (n = 3). The values obtained from experiments are shown mean ± SD. FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; hMSC-EVs: Human mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles, NTA: Nanoparticle tracking analysis.