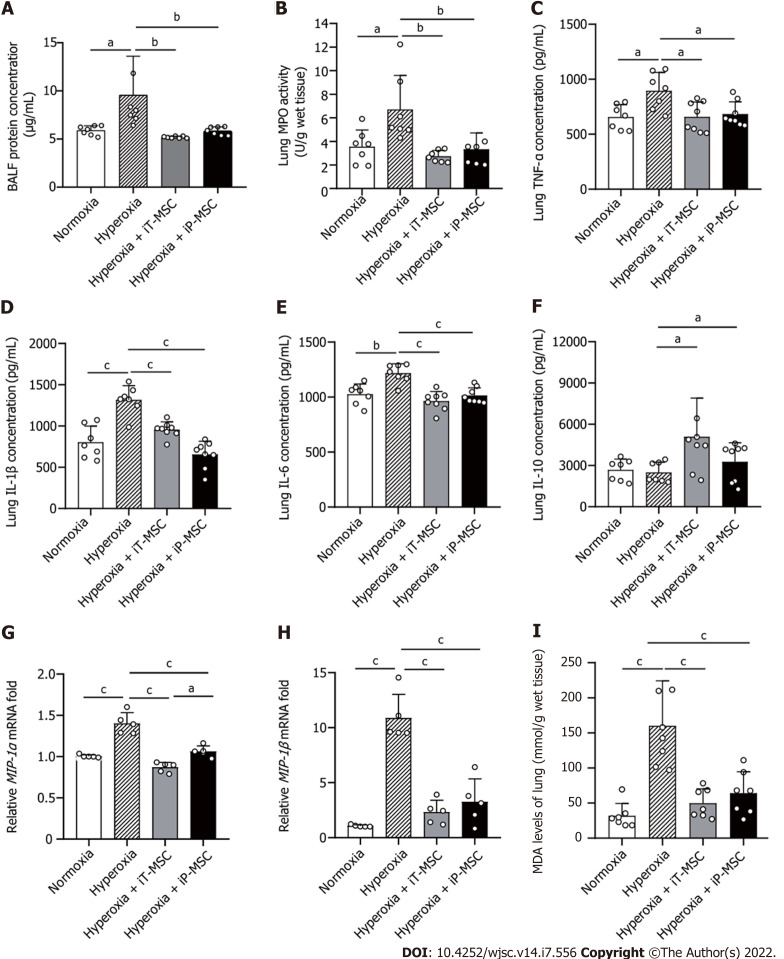
Figure 4.
Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells treatment modulates the hyperoxia-induced lung inflammation and oxidative stress. A: Statistical analyses of overall protein concentration in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in the four groups (n = 7); B-F: Statistical analyses of myeloperoxidase, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and IL-10 levels in the lung tissues in the indicated groups (n = 7); G and H: Macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1α and MIP-1β mRNA expression in the indicated groups (n = 5); I: Malondialdehyde levels were measured to evaluate the degree of oxidative reaction in the lung tissues (n = 7). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. iT: Intratracheal; iP: Intraperitoneal; BALF: Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL: Interleukin; MIP: Macrophage inflammatory protein; MDA: Malondialdehyde; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell.