Figure 5.
High-affinity antibody restricts VRC01-precursor responses
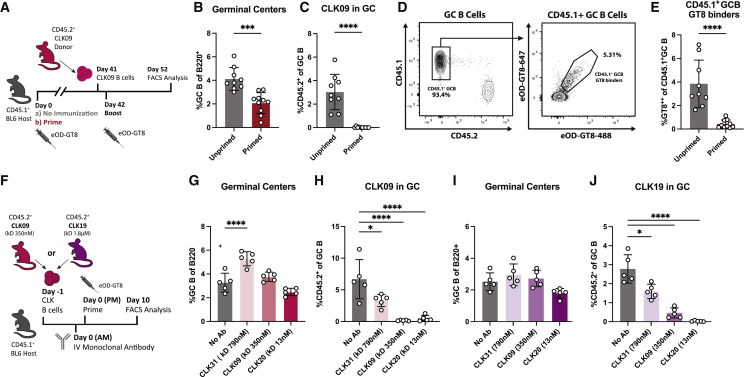
(A) Schematic of experiment to evaluate naive CLK09 B cell responses in primed and unprimed recipients.
(B and C) (B) GC cells as the percentage of total B cells and (C) CD45.2+ CLK09 cells as the percentage of total GC B cells at experiment day 52 (10 dpi) in previously unprimed (gray) or primed (red) recipients.
(D) Representative FACS plots at experiment day 52 (10 dpi) of gating strategy to quantify eOD-GT8 binding in the endogenous CD45.1+ GC B cell population.
(E) eOD-GT8 binding of endogenous CD45.1+ GC B cells at experiment day 52 (10 dpi) in unprimed and primed hosts.
(F) Schematic of experiment to evaluate the effects of i.v. administration of 10 μg of CLK mAbs with increasing affinity for the eOD-GT8 immunogen (CLK31 with KD 790 nM, CLK09 with KD 350 nM, and CLK20 with KD 13 nM) on naive CLK09 and CLK19 B cell responses in WT recipients (G–J).
(G and H) (G) GC cells as the percentage of total B cells and (H) CD45.2+ CLK09 cells as the percentage of total GC B cells at 10 dpi of CLK09 recipients.
(I and J) (I) GC cells as the percentage of total B cells and (J) CD45.2+ CLK19 cells as the percentage of total GC B cells at 10 dpi of CLK19 recipients.
p values were calculated by unpaired Student’s t test (B, C, and E) or ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons (G–J) (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ns, not significant). Figures represent data from one of at least two experiments with 3–5 mice per condition, with data presented as mean ± SD.
See also Figure S6.