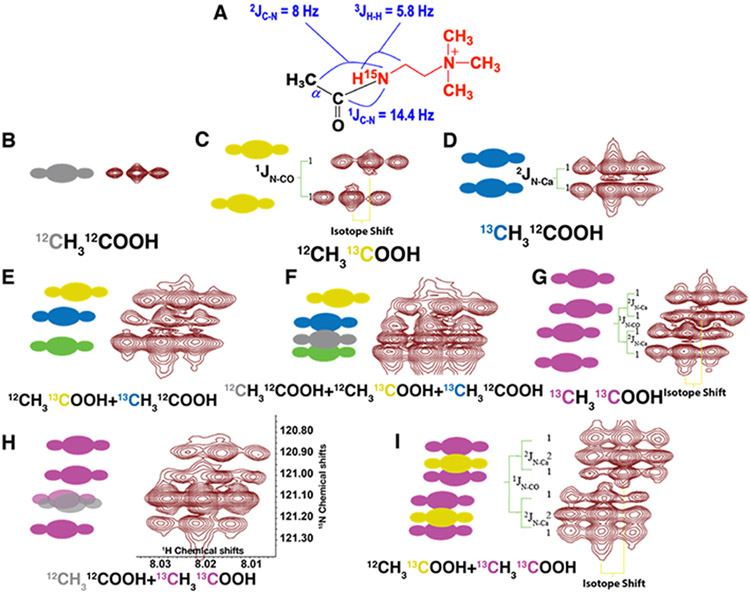
Figure 3. Simulated and observed cross-peak splitting patterns in 2D 1H{15N}-HSQC spectra of different mixtures of acetate isotopomers.
A) Structure of the product of acetate reacted with 15N-cholamine showing the different coupling constants between 13C-15N and 1HN-1H. B-I) Side by side comparison of the simulated and observed peak patterns of different acetate isotopomer mixtures. The following peak patterns are evident in the 15N dimension: 12CH312CO2- a singlet (B), 12CH313CO2- a doublet with 1JCN = 14.4 Hz (C), 13CH312CO2- a doublet with 2JCN = 8 Hz (D), 12CH313CO2- + 13CH312CO2- two overlapping doublets or an apparent triplet (E), 12CH313CO2- + 13CH312CO2- + 12CH312CO2- an apparent triplet plus singlet (F), 13CH313CO2- a doublet of doublet (G); 12CH312CO2- + 13CH313CO2- a doublet of doublet plus overlapping singlet (H), and 12CH313CO2- + 13CH313CO2- a doublet of doublet plus a doublet (I). Different colors indicate different 13C label positions in the acetate isotopomers: Gray, 12C; Yellow, 13CO; Blue, 13CA; Purple, 13CO-13CA; Green, overlapping of yellow and blue peaks. Pixels are scaled to the coupling constants to accurately represent the splitting patterns. The chemical shift scales in both dimensions are shown in panel H, which is the same for all panels.