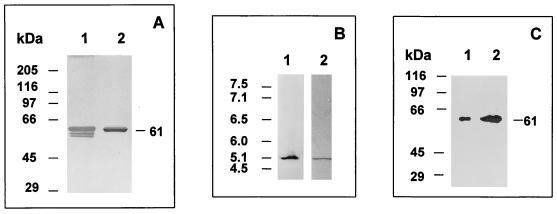
FIG. 2.
Homogeneity and integrity of purified BADH from P. aeruginosa. (A) SDS-PAGE (8% gel) and silver staining of the purified BADH (0.44 μg of protein). Lane 1, enzyme purified with β-mercaptoethanol in buffer and loaded after mixing with a sample buffer without a reducing agent. Lane 2, same as lane 1 but with 5 mM DTT in the sample buffer. The following proteins were used as Mr standards: rabbit muscle myosin (205,000), E. coli β-galactosidase (116,000), rabbit muscle phosphorylase b (97,400), bovine plasma albumin (66,000), ovalbumin (45,000), and bovine erythrocyte carbonic anhydrase (29,000). (B) Nondenaturing isoelectric focusing gel of BADH in cell extracts (22 μg of protein) (lane 1) and denaturing isoelectric focusing gel of purified BADH (5.0 μg of protein) in the presence of 8 M urea and 5 mM DTT (lane 2). Lane 1 was activity stained, and lane 2 was stained with Coomassie blue. The following proteins were used as pI standards: human hemoglobin C (7.5), human hemoglobin A (7.1), human carbonic anhydrase (6.5), bovine carbonic anhydrase (6.0), β-lactoglobulin B (5.1), and phycocyanin (4.5). The pIs of the standards are shown on the left. (C) Western blots of purified BADH (0.25 μg of protein) (lane 1) and BADH in cell extracts from P. aeruginosa grown in choline (38 μg of protein) (lane 2). Samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE (8% gel), transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and probed with anti-Pseudomonas BADH antibody.