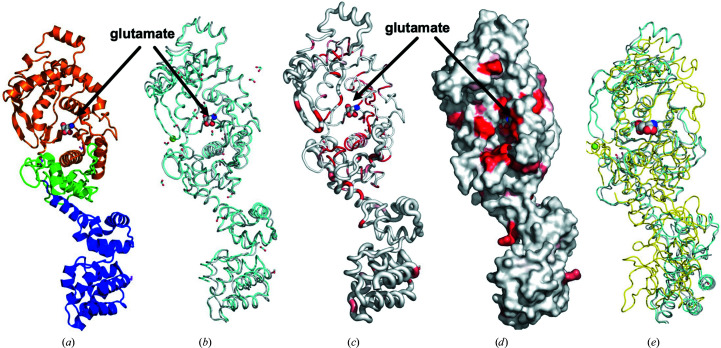
Figure 1.
Structures of EmGluRS and EaGluRS. (a) The EmGluRS monomer has a Rossmann fold (orange), a zinc-binding domain (green) and an anticodon-binding domain (blue). The Rossmann fold and zinc-binding domain make up the N-terminal tRNA synthetase binding domain that binds the glutamate (spheres). (b) Superposed structures of EmGluRS (gray) and EaGluRS (cyan). The Mg2+ ion in EaGluRS is shown as a green sphere, the glutamate molecule is shown as spheres (C atoms in gray, O atoms in red and N atoms in blue) and formate and ethylene glycol from crystallization are shown as sticks. (c) Ribbon diagram calculated by ENDScript. The circumference of the ribbon (sausage) represents the relative structural conservation compared with other GluRS structures (these structures are indicated in Supplementary Fig. S2). Thinner ribbons represent more highly conserved regions, while thicker ribbons represent less conserved regions. (d) Solvent-accessible surface area of EmGluRS colored by sequence conservation, with red indicating identical residues. (e) Superposed structures of PaGluRS (PDB entry 5tgt, yellow), EmGluRS (gray) and EaGluRS (cyan). The sequence alignment of PaGluRS is shown in Fig. 3 ▸.