Figure 2. Factor XII Structure.
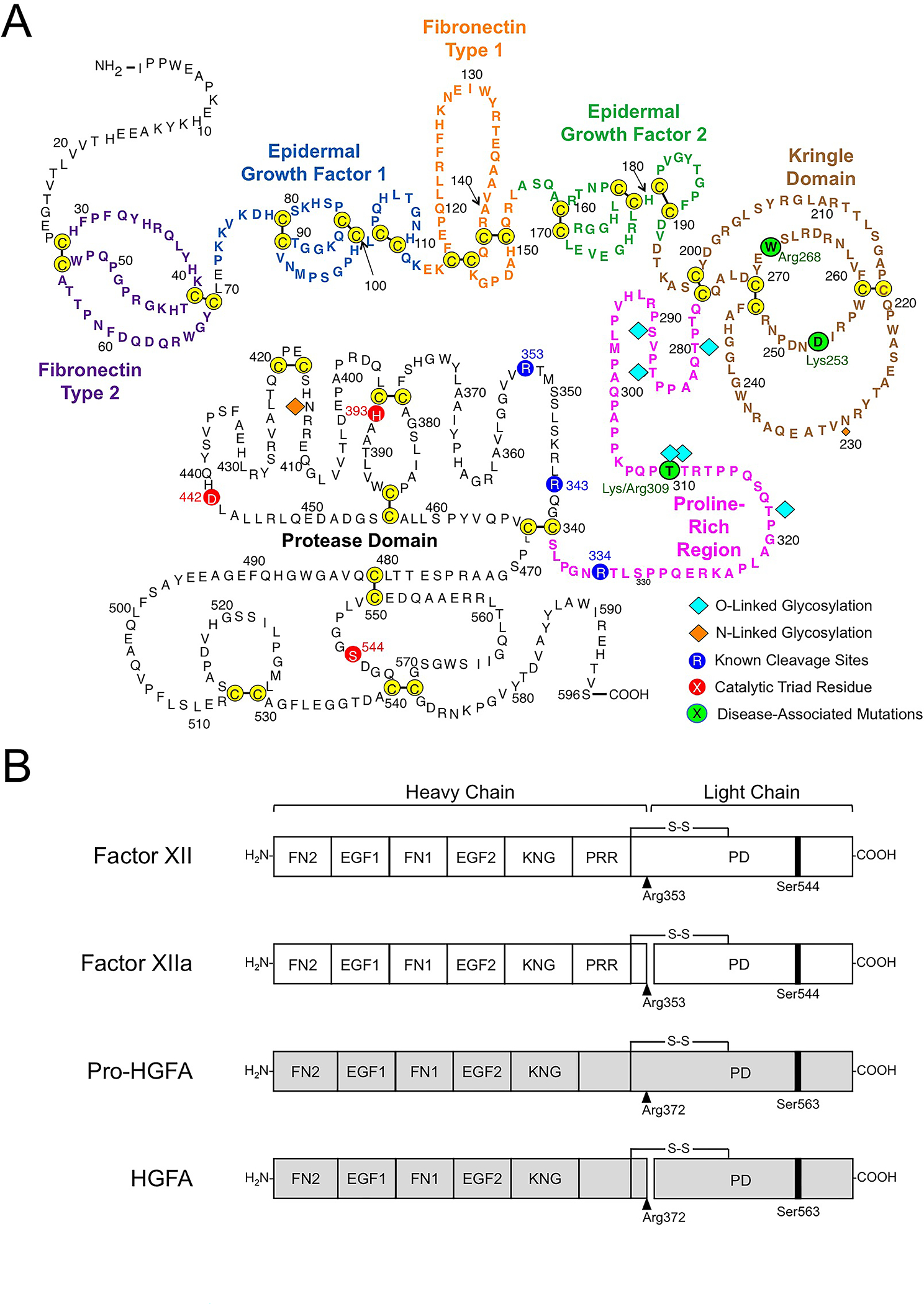
(A) Amino acid sequence and disulfide bonds for human plasma FXII. The heavy chain contains a fibronectin type 2 (purple), epidermal growth factor 1 (blue), fibronectin type 1 (orange), epidermal growth factor 2 (green), and kringle (brown) domain, and a proline-rich regions (magenta). The catalytic triad His393, Asp442 Ser544 in the protease domain (light chain) are indicated in red. Positions of O- and N-linked glycosylation sites are indicated by blue and orange diamonds. Positions of disease-associated mutations are shown in green circles. Image adapted from reference 27. (B) Schematic diagrams of human FXII (white), Pro-HGFA (gray), and their activated forms FXIIa and HGFA. The FXII fibronectin type 2 (FN2), epidermal growth factor 1 (EGF1), fibronectin type 1 (FN1), epidermal growth factor 2 (EGF2), and kringle (KNG) domains, the proline-rich region (PRR), and the protease domain are indicated. Pro-HGFA is organized similarly except that it does not have a PRR, and the corresponding sequence is not assigned a name. Positions of FXII and Pro-HGFA active site serine residues (Ser544 and Ser563, respectively) are indicated by black bars, and sites for proteolytic activation (after Arg353 and Arg372, respectively) are indicated by black arrows. Image adapted from reference 2.
